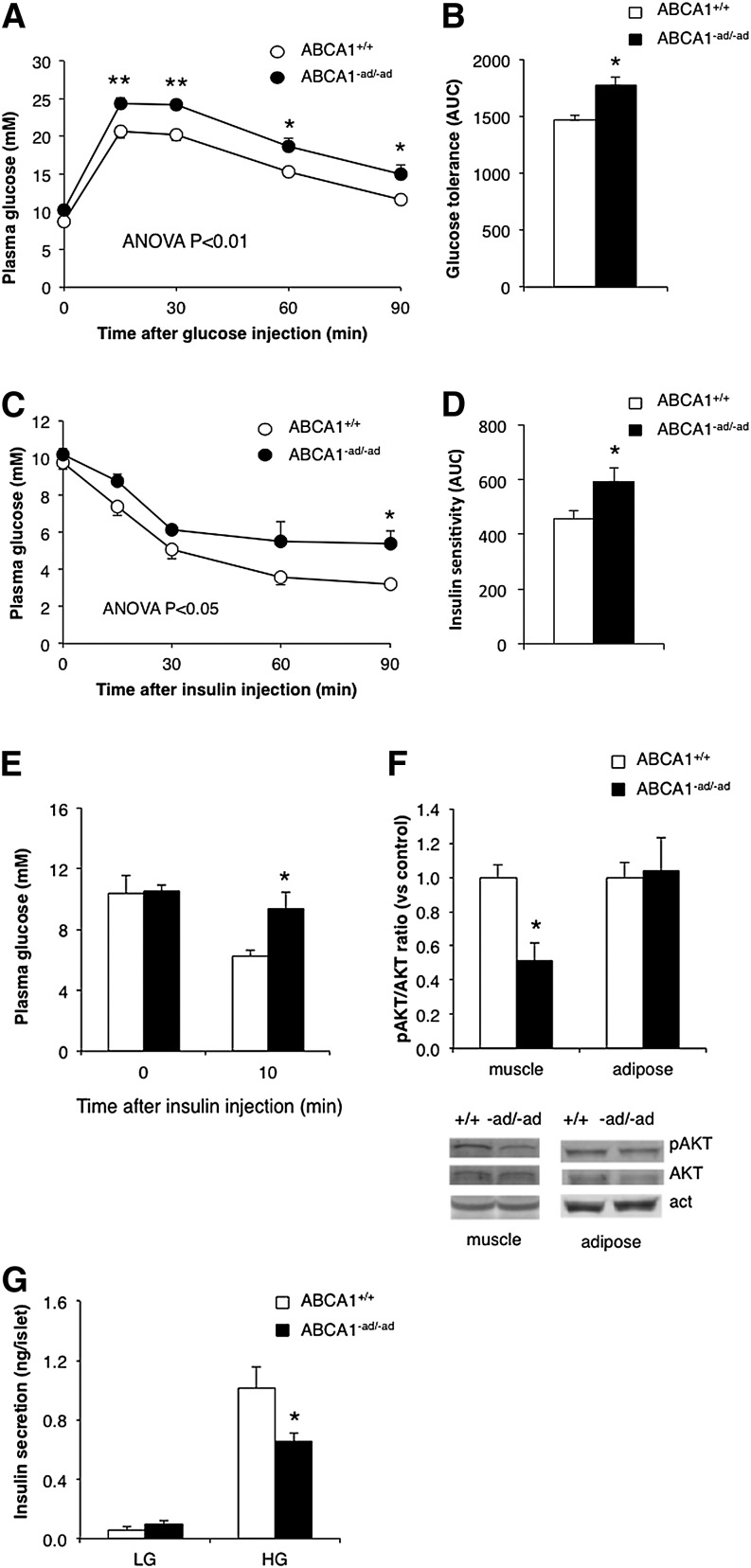
Fig. 5.
Adipocyte ABCA1 deficiency impairs glucose tolerance. ABCA1+/+ mice and ABCA1−ad/−ad mice fed an HFHC diet received an intraperitoneal injection of 1 g/kg glucose in PBS, blood samples were drawn at the indicated time points, and glucose was measured to assess glucose tolerance (A, B). Insulin sensitivity was assessed by injecting mice intraperitoneally with 1 U/kg insulin in PBS, and glucose was measured at the indicated time points (C, D). To assess tissue-specific insulin sensitivity, mice were injected with 10 U/kg insulin, tissues were isolated, and pAKT and total AKT levels were measured by Western blotting (E, F). Pancreatic islets were isolated from ABCA1+/+ mice and ABCA1−ad/−ad mice fed an HFHC diet and incubated in low- (1.67 mM) and high-glucose (16.7 mM) medium, and insulin secretion was measured (G). Values are means ± SEM; N = 6–7 (A–D), N = 3–4 (E, F), N = 10–13 (G). * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.