Figure 2. Three distinct RHIM complexes trigger RIP3 necrosis.
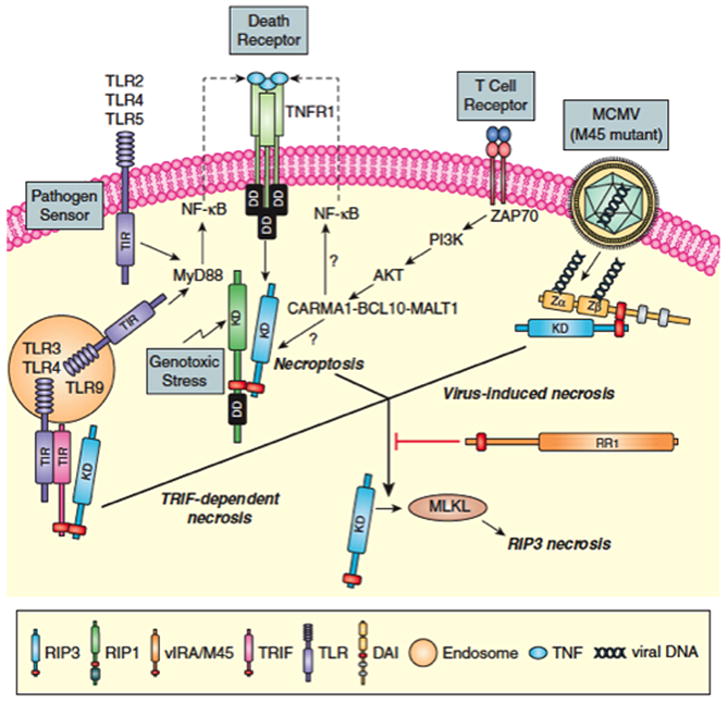
RIP1-RIP3 necroptosis first characterized downstream of death receptor activation via RIP1-RIP3 complex formation (37–39) is also induced by pathogen sensor (e.g. TLR2, TLR4, TLR5 or TLR9 MyD88-dependent signaling) (27, 28), TCR activation (32, 33), intracellular genotoxic stress (34) and vaccinia virus infection (37). Virus-induced DAI-RIP3 necrosis (3, 25, 26) is activated by MCMV M45 mutant virus infection. TRIF-RIP3 necrosis in fibroblasts is activated TLR3 or TRL4 ligands (27, 28). RIP3 complexes with RIP1, DAI or TRIF depend on RHIM interactions that activate RIP3 kinase-dependent modification of MLKL (7, 41, 42) (see Fig. 1). MCMV M45-encoded vIRA functions as a dominant RHIM-inhibitor preventing RIP3 association with RIP1, DAI or TRIF.
