Figure 1. Inhibition of the JAK/STAT Pathway Suppresses Th1 and Th17 Cell Differentiation In Vitro.
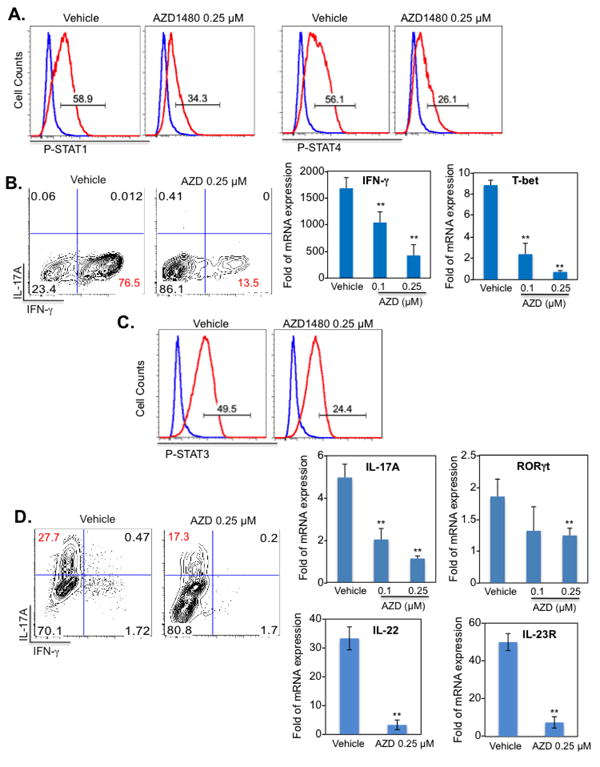
Naïve CD4+ T-cells were isolated from the spleen of C57BL/6 mice. Dendritic cells (DCs) were used as antigen-presenting cells at a 1:5 ratio to CD4+ T-cells in co-culture. Vehicle control or AZD1480 (0.25 μM) was added simultaneously to the Th1 or Th17 differentiation cocktail. (A). Th1 cells were differentiated with anti-CD3 (1 μg/ml), anti-CD28 (1 μg/ml), IL-12 (10 ng/ml) plus anti-IL-4 Ab (10 μg/ml) for 4 days. STAT1 and STAT4 tyrosine phosphorylation was examined by flow cytometry (red line) with isotype control shown in blue. (B). At day 4, cells were stimulated with PMA/Ionomycin plus GolgiStop for 4 h, stained for the surface marker CD4 and by intracellular flow to detect IFN-γ expression. For mRNA expression, cells were collected at day 4, and mRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR for IFN-γ and T-bet. (C). Th17 cells were differentiated with anti-CD3 (1 μg/ml), anti-CD28 (1 μg/ml), TGF-β (5 ng/ml), IL-6 (20 ng/ml), IL-23 (10 ng/ml) plus anti-IFN-γ Ab (10 μg/ml) and anti-IL-4 Ab (10 μg/ml) for 4 days. STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation (red line) was examined by flow cytometry, with isotype control shown in blue. (D). At day 4, cells were stimulated with PMA/Ionomycin plus GolgiStop for 4 h, stained for the surface marker CD4 and by intracellular flow to detect IL-17A expression. For mRNA expression, cells were collected at day 4, and mRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR for IL-17A, RORγt, IL-22 and IL-23R. *p<0.05 and **p<0.001.
