Figure 4. The anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was significantly increased and pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α were decreased in the cortex of KO/Tg mice brains compared to WT/Tg mice brains at 14 months old.
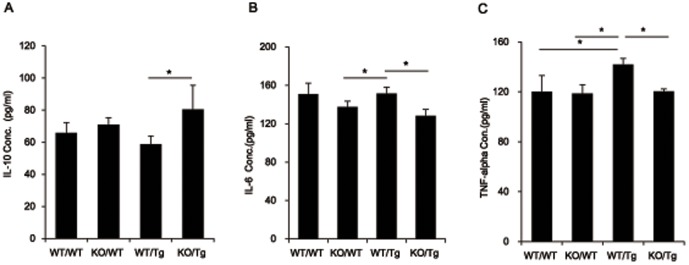
(A) The level of IL-10 was detected in the tissue lysates from the cortical region of the brain from each group by sandwich ELISA. IL-10, which is a representative anti-inflammatory cytokine, was increased in the cortex of KO/Tg mice brains compared to WT/Tg mice brains. (B) The level of IL-6 was detected in the tissue lysates from the cortical region of the brain from each group by sandwich ELISA. IL-6, which is a representative pro-inflammatory cytokine, was decreased in the cortex of KO/Tg mice brains compared to WT/Tg mice brains. (C) The level of TNF-α was detected in the tissue lysates from the cortical region of the brain from each group by sandwich ELISA. TNF-α, which is a representative pro-inflammatory cytokine, was decreased in the cortex of KO/Tg mice brains compared to WT/Tg mice brains. (n = 9–10), *p<0.05 by one-way ANOVA.
