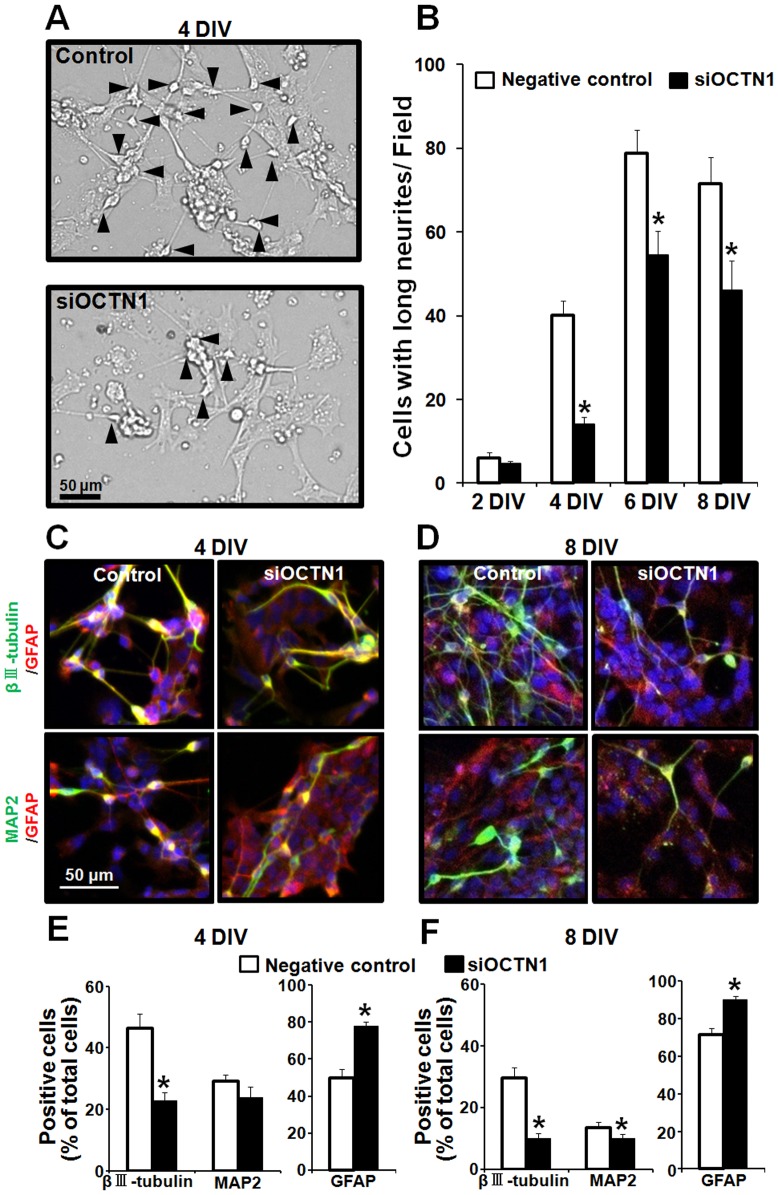
Figure 7. Effect of OCTN1 knockdown on differentiation of P19-NPCs.
P19 cells were cultured in the presence of retinoic acid for 3-NPCs, and siRNA for OCTN1 or negative control siRNA was transiently transfected. Adhesion culture was started at 3 DIV after the transfection to induce differentiation into neurons and astrocytes. (A) Adhesion culture was maintained for 4 to 8 DIV, and typical phase-contrast micrographs are shown. Black arrowheads represent differentiated neuron-like cells with neurites longer than the cell diameter. (B) The numbers of differentiated cells per field were counted for 8 DIV in P19-NPCs after the transfection of siOCTN1 (black columns) or negative control siRNA (white columns). Each value represents the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 15). (C, D) P19-NPCs transfected with siOCTN1 or negative control were induced to differentiate by adhesion culture for 4 or 8 DIV, and then the cells were fixed with 4% PA, followed by immunocytochemical detection of immature neuronal marker βIII-tubulin (green), mature neuronal marker MAP2 (green), astroglial marker GFAP (red) and nuclear marker DAPI (blue). (E, F) The numbers of cells positive for each marker were counted by using ImageJ and normalized by the number of DAPI-positive cells. Each value represents the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 8). *P<0.05, significant difference from the corresponding control value.