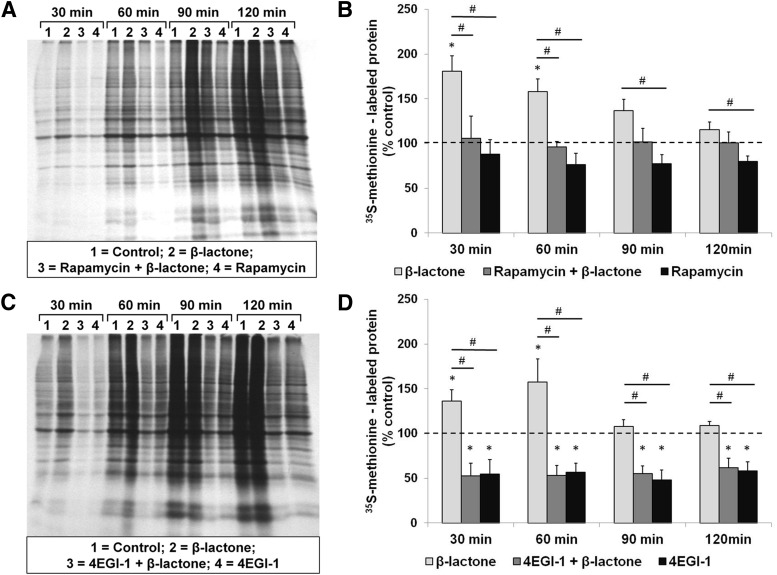
Figure 10.
β-Lactone enhances the quantity of newly translated proteins in hippocampal slices and the enhancement is blocked by rapamycin and 4EGI-1. Autoradiographs (A and C) showing incorporation of 35S-methionine at 30, 60, 90, and 120 min after initiation of metabolic labeling indicating the amount of newly synthesized proteins when the hippocampal slices are treated with β-lactone by itself or after prior treatment with rapamycin (A) or 4EGI-1 (C). Quantification shows that rapamycin (B) and 4EGI-1 (D) block the β-lactone-mediated increase in 35S-methionine-labeled proteins (lanes 2 compared with lanes 3 in A and C and second bars compared with first bars in B and D). Effect of rapamycin alone or 4EGI-1 alone on control slices (lanes 4 in A and C and third bars in B and D) is also shown. *p < 0.05 compared with controls (depicted by a dashed line). #p < 0.05 comparison between two given experimental conditions as indicated by horizontal lines.