Abstract
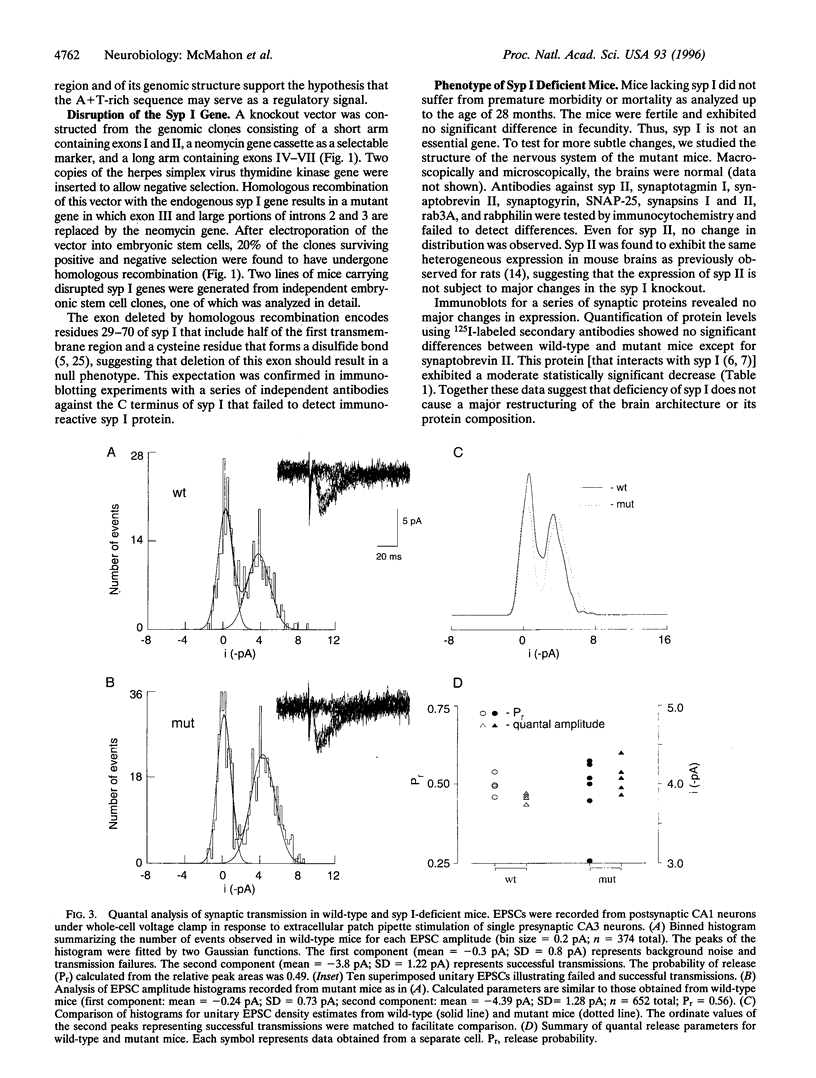
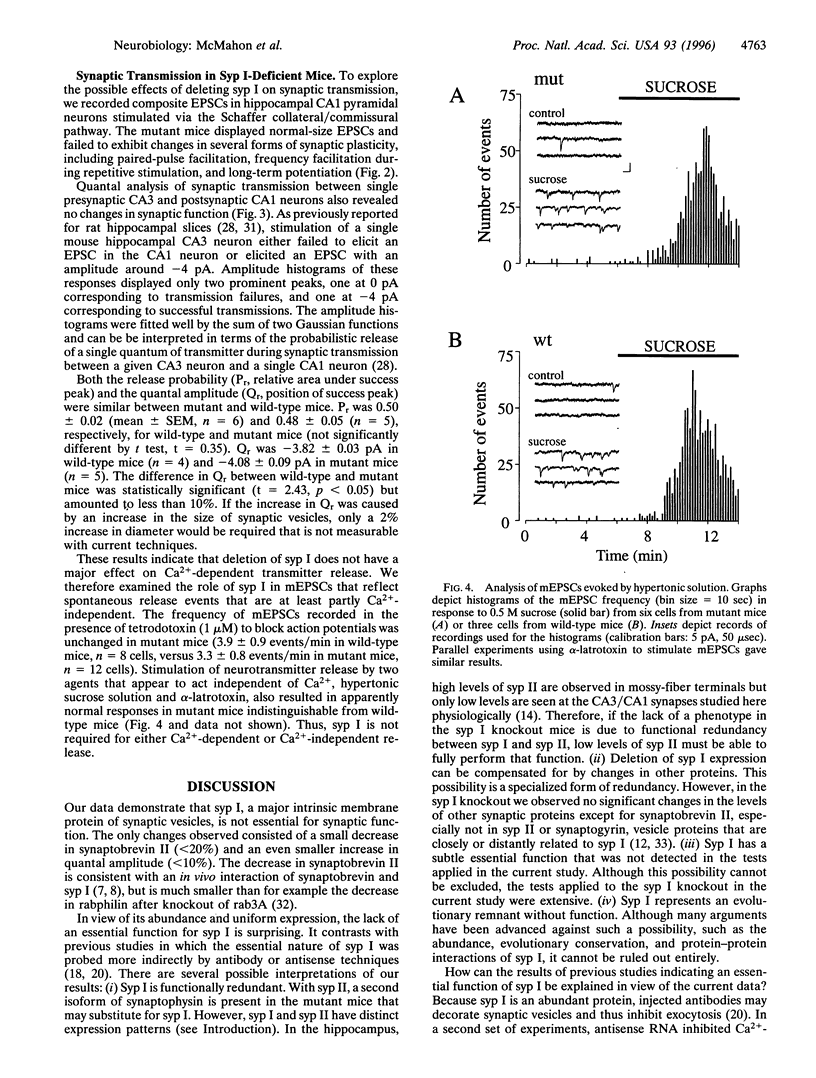
Synaptophysin (syp I) is a synaptic vesicle membrane protein that constitutes approximately 7% of the total vesicle protein. Multiple lines of evidence implicate syp I in a number of nerve terminal functions. To test these, we have disrupted the murine Syp I gene. Mutant mice lacking syp I were viable and fertile. No changes in the structure and protein composition of the mutant brains were observed except for a decrease in synaptobrevin/VAMP II. Synaptic transmission was normal with no detectable changes in synaptic plasticity or the probability of release. Our data demonstrate that one of the major synaptic vesicle membrane proteins is not essential for synaptic transmission, suggesting that its function is either redundant or that it has a more subtle function not apparent in the assays used.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alder J., Kanki H., Valtorta F., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Overexpression of synaptophysin enhances neurotransmitter secretion at Xenopus neuromuscular synapses. J Neurosci. 1995 Jan;15(1 Pt 2):511–519. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00511.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alder J., Lu B., Valtorta F., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Calcium-dependent transmitter secretion reconstituted in Xenopus oocytes: requirement for synaptophysin. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):657–661. doi: 10.1126/science.1353905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alder J., Xie Z. P., Valtorta F., Greengard P., Poo M. Antibodies to synaptophysin interfere with transmitter secretion at neuromuscular synapses. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90038-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnekow A., Jahn R., Schartl M. Synaptophysin: a substrate for the protein tyrosine kinase pp60c-src in intact synaptic vesicles. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1019–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolshakov V. Y., Siegelbaum S. A. Postsynaptic induction and presynaptic expression of hippocampal long-term depression. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1148–1152. doi: 10.1126/science.7909958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolshakov V. Y., Siegelbaum S. A. Regulation of hippocampal transmitter release during development and long-term potentiation. Science. 1995 Sep 22;269(5231):1730–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.7569903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brose N., Petrenko A. G., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Synaptotagmin: a calcium sensor on the synaptic vesicle surface. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1021–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.1589771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Vesicle-associated membrane protein and synaptophysin are associated on the synaptic vesicle. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24534–24537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli A., Eder-Colli L., Dunant Y., Loctin F., Morel N. Release of acetylcholine by Xenopus oocytes injected with mRNAs from cholinergic neurons. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1671–1675. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann L., Hanson P. I., Chapman E. R., Jahn R. Synaptobrevin binding to synaptophysin: a potential mechanism for controlling the exocytotic fusion machine. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):224–231. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fykse E. M., Takei K., Walch-Solimena C., Geppert M., Jahn R., De Camilli P., Südhof T. C. Relative properties and localizations of synaptic vesicle protein isoforms: the case of the synaptophysins. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4997–5007. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04997.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppert M., Bolshakov V. Y., Siegelbaum S. A., Takei K., De Camilli P., Hammer R. E., Südhof T. C. The role of Rab3A in neurotransmitter release. Nature. 1994 Jun 9;369(6480):493–497. doi: 10.1038/369493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Cameron P. L., Stukenbrok H., Jahn R., De Camilli P., Südhof T. C. Synaptophysin is targeted to similar microvesicles in CHO and PC12 cells. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2863–2872. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Transmembrane topography and evolutionary conservation of synaptophysin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus P., Marquèze-Pouey B., Scherer H., Betz H. Synaptoporin, a novel putative channel protein of synaptic vesicles. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90084-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Kaiser P., Seiter A., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W., Rehm H., Knaus P., Prior P., Betz H., Reinke H. Synaptophysin: molecular organization and mRNA expression as determined from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3261–3268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Topogenesis and sorting of synaptophysin: synthesis of a synaptic vesicle protein from a gene transfected into nonneuroendocrine cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):433–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linstedt A. D., Vetter M. L., Bishop J. M., Kelly R. B. Specific association of the proto-oncogene product pp60c-src with an intracellular organelle, the PC12 synaptic vesicle. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):1077–1084. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquèze-Pouey B., Wisden W., Malosio M. L., Betz H. Differential expression of synaptophysin and synaptoporin mRNAs in the postnatal rat central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3388–3397. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03388.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Südhof T. C. Synaptic core complex of synaptobrevin, syntaxin, and SNAP25 forms high affinity alpha-SNAP binding site. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 3;270(5):2213–2217. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.2213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozçelik T., Lafreniere R. G., Archer B. T., 3rd, Johnston P. A., Willard H. F., Francke U., Südhof T. C. Synaptophysin: structure of the human gene and assignment to the X chromosome in man and mouse. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Sep;47(3):551–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Wang J. K., Valtorta F., Benfenati F., Greengard P. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):762–766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehm H., Wiedenmann B., Betz H. Molecular characterization of synaptophysin, a major calcium-binding protein of the synaptic vesicle membrane. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):535–541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosahl T. W., Spillane D., Missler M., Herz J., Selig D. K., Wolff J. R., Hammer R. E., Malenka R. C., Südhof T. C. Essential functions of synapsins I and II in synaptic vesicle regulation. Nature. 1995 Jun 8;375(6531):488–493. doi: 10.1038/375488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Greengard P., Czernik A. J. Calcium-dependent serine phosphorylation of synaptophysin. Synapse. 1993 Feb;13(2):161–172. doi: 10.1002/syn.890130207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenius K., Janz R., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Structure of synaptogyrin (p29) defines novel synaptic vesicle protein. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1801–1809. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F., Wang Y. Facilitation and depression at single central synapses. Neuron. 1995 Apr;14(4):795–802. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Lottspeich F., Greengard P., Mehl E., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle protein with a novel cytoplasmic domain and four transmembrane regions. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1142–1144. doi: 10.1126/science.3120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C. The structure of the human synapsin I gene and protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7849–7852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Hartung K., Langosch D., Rehm H., Bamberg E., Franke W. W., Betz H. Identification of synaptophysin as a hexameric channel protein of the synaptic vesicle membrane. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1050–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.2461586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



