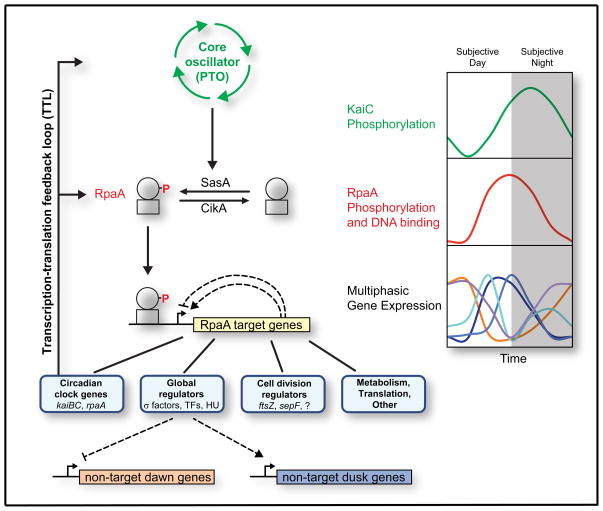
Figure 7. Model for RpaA and the cyanobacterial circadian program.
Model for control of clock output by RpaA. Time encoded in the PTO is transduced into RpaA phosphorylation via SasA and CikA, producing oscillations in RpaA~P (red) that phase-lead those of phosphorylated KaiC (green) by approximately 4 hours (Gutu and O’Shea, 2013). RpaA~P binds to DNA and controls the expression of the RpaA regulon, which consists of global regulators, cell division regulators, certain clock genes (kaiBC and rpaA), and genes involved in metabolism and translation. The global regulators are at the top of a transcriptional cascade that orchestrates multiphasic circadian gene expression, repressing subjective dawn genes while activating subjective dusk genes. Fine patterns within the dusk and dawn categories could be generated by a network of interactions amongst RpaA ChIP targets (hypothetical positive and negative feedbacks are shown as dotted lines). RpaA control of kaiBC and rpaA expression forms the clock TTL.