Figure 2.
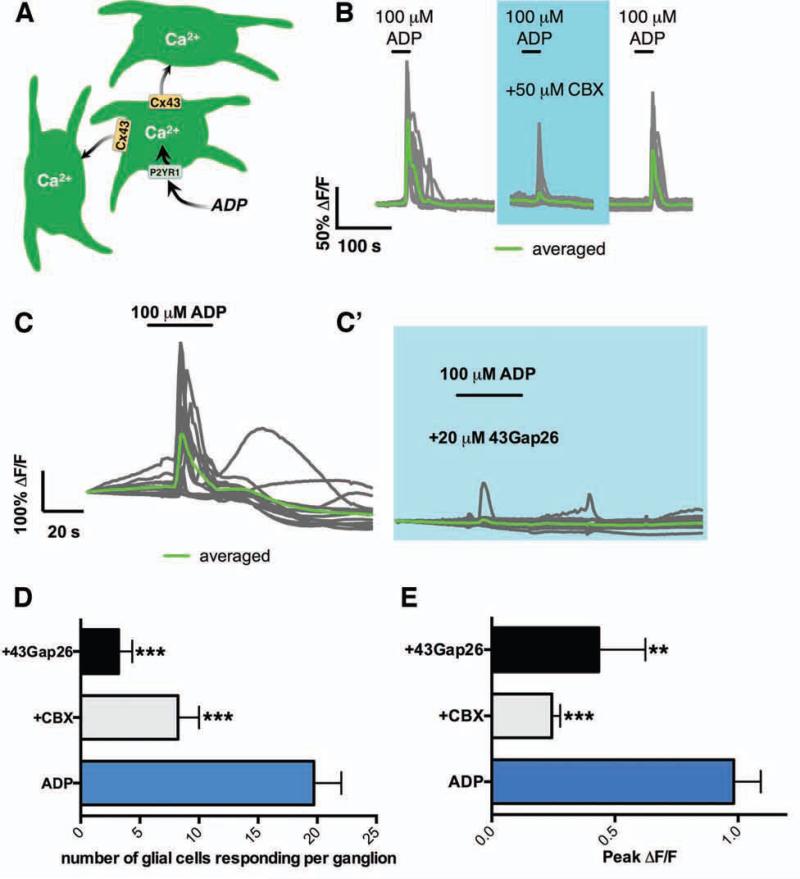
Purine–evoked Ca2+ waves between EG depend on Cx43. (A) Model of purine–evoked Ca2+ responses through the EG network. (B) Representative traces of Ca2+ response evoked by ADP (30 s, 100 μM) in the presence or absence of the Cx43 antagonist, carbenoxolone (CBX; 50 μM; blue shaded area) in 21 EG within a myenteric ganglion (gray traces, average in green). Note that CBX limits the number of responding glia and on average, the Ca2+ response is lost. Glial responses recover upon washout of drug. (C) Representative Ca2+ response evoked by ADP in 13 EG within a myenteric ganglion (gray traces, average in green) in the presence or absence of the specific Cx43 mimetic peptide, 43Gap26 (20 μM). Effect of CBX and 43Gap26 on (D) the number of glia responding to ADP per ganglion and (E) peak glial Ca2+ responses (n=5-14, ***P=.0001, ANOVA).