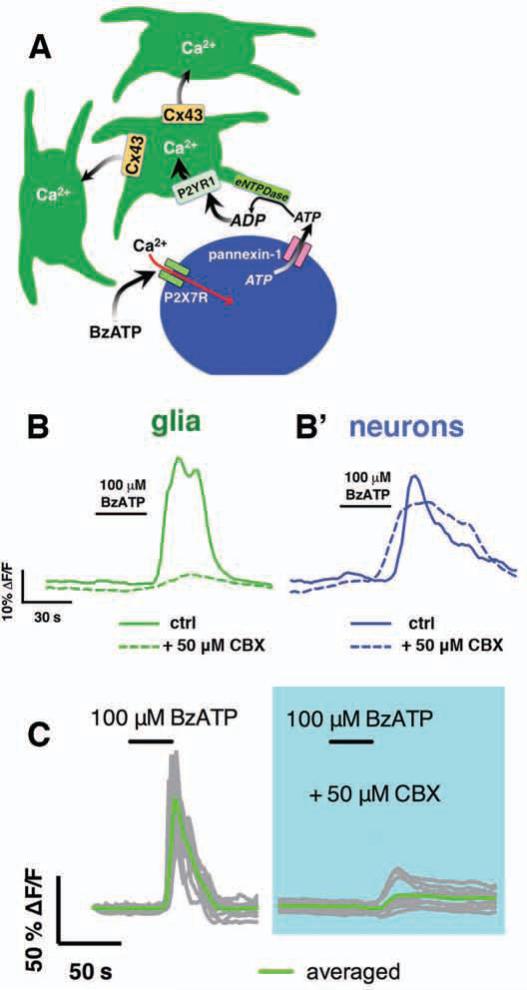
Figure 3.
EG Ca2+ waves evoked by enteric neuron–to–glia communication depend on Cx43. (A) Model depicting how pharmacological activation of enteric neurons initiates Ca2+ responses in EG. (B) Representative traces of average Ca2+ response in glia (green traces) and neurons (blue traces) within a myenteric ganglion following stimulation of enteric neuron–to–glia communication with the P2X7 agonist, BzATP (100 μM). Note that both neurons and glia respond in control (solid traces) but glial responses are lost when Cx43 is inhibited with CBX (50 μM; dashed traces). (C) Representative Ca2+ wave evoked through 12 glia within a myenteric ganglion (gray traces, average in green) by stimulating enteric neuron–glia communication with BzATP in the presence or absence of CBX.