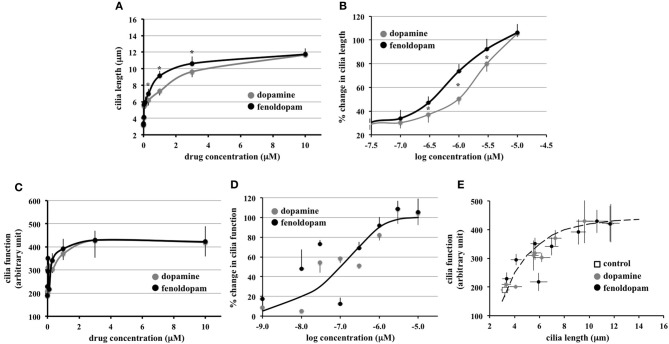
Figure 3.
Function of primary cilia as sensory organelles depends on the length of cilia. (A) Hyperbolic curves indicated a positive correlation between cilia length and dopamine or fenoldopam. Averaged cilia length is shown from cells treated with dopamine or fenoldopam at 1 nM to 10 μ M. (B) Sigmoidal curves were generated with logarithmic transformation to indicate a cause-and-effect relationship between cilia length and dopamine or fenoldopam. (C) Hyperbolic curves indicated a positive correlation between cilia function and dopamine or fenoldopam. Cilia function was demonstrated by calcium signaling induced by fluid-shear stress. Averaged cilia function is shown from cells treated with dopamine or fenoldopam at 1 nM to 10 μ M. (D) Sigmoidal curves were generated with logarithmic transformation to indicate a cause-and-effect relationship between cilia function and dopamine or fenoldopam. (E) Peak calcium changes were averaged in cells treated with mock (control), dopamine, or fenoldopam at 1 nM to 10 μ M. A hyperbolic curve indicates a positive correlation between cilia length and function. Asterisks denote significant difference at p < 0.05. N = 28 for each dopamine or fenoldopam treatment.