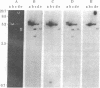
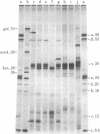
Abstract
The chromosomal replication origin (oriC) of Vibrio harveyi has been isolated on a plasmid and shown to function as an origin in Escherichia coli. The nucleotide sequence of the V. harveyi oriC was determined. From a comparison of this sequence with oriC sequences of five enteric bacteria, we derived a consensus sequence of bacterial origins that function in E. coli. This consensus sequence identifies 122 positions within oriC where nucleotide substitutions can occur without loss of origin function. These positions are clustered rather than scattered. Four interrelated nine-base-pair repeats and eight of the dam methylation G-A-T-C sites are conserved in the consensus sequence. Very few relative insertion-deletion changes occur, and these are localized to one region of oriC. The genes for three polypeptides linked to the V. harveyi oriC were identified by using in vitro protein synthesis directed by deletion derivative plasmid templates. One of these genes, coding for a 58,000 Mr polypeptide and located 3.0 kilobase pairs from the V. harveyi oriC region, is lethal to E. coli when many copies (approximately 40 per cell) are present (high copy lethal or HCL gene). In addition, nucleotide sequence analysis showed that a different gene, the gid gene to the left of oriC, is highly conserved between E. coli and V. harveyi, whereas the coding region to the right of oriC is much less conserved.
Full text
PDF
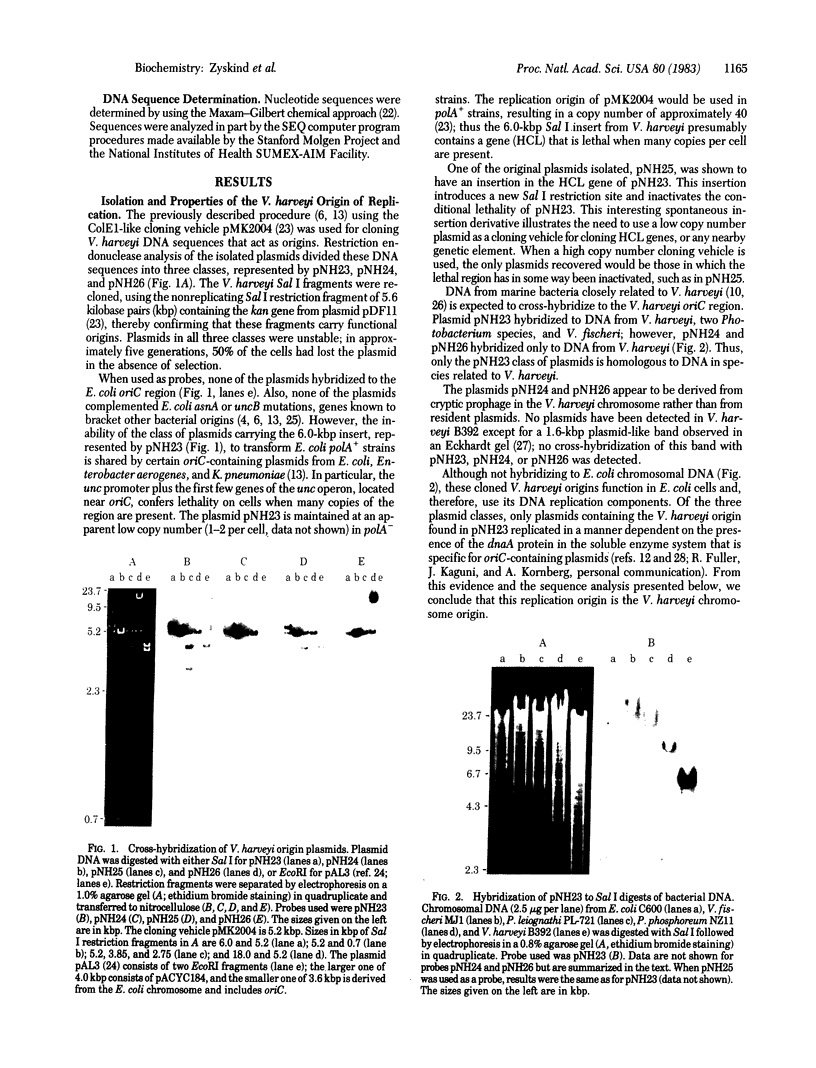



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann P., Baumann L. Biology of the marine enterobacteria: genera Beneckea and Photobacterium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:39–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary J. M., Smith D. W., Harding N. E., Zyskind J. W. Primary structure of the chromosomal origins (oriC) of Enterobacter aerogenes and Klebsiella pneumoniae: comparisons and evolutionary relationships. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1467–1471. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1467-1471.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Kaguni J. M., Kornberg A. Enzymatic replication of the origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7370–7374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Brusilow W. S., Simoni R. D. Gene order and gene-polypeptide relationships of the proton-translocating ATPase operon (unc) of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):320–324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding N. E., Cleary J. M., Smith D. W., Michon J. J., Brusilow W. S., Zyskind J. W. Chromosomal replication origins (oriC) of Enterobacter aerogenes and Klebsiella pneumoniae are functional in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):983–993. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.983-993.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni J. M., Fuller R. S., Kornberg A. Enzymatic replication of E. coli chromosomal origin is bidirectional. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):623–627. doi: 10.1038/296623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynan A., Nealson K., Sideropoulos H., Hastings J. W. Marine transducing bacteriophage attacking a luminous bacterium. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.333-340.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lark K. G. Evidence for the direct involvement of RNA in the initiation of DNA replication in Escherichia coli 15T. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lother H., Messer W. Promoters in the E. coli replication origin. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):376–378. doi: 10.1038/294376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer M., Beck E., Hansen F. G., Bergmans H. E., Messer W., von Meyenburg K., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence of the origin of replication of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):580–584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. Bacterial bioluminescence: its control and ecological significance. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):496–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.496-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugimoto K., Takanami M., Hirota Y. Replication origin of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome: the size and structure of the minimum DNA segment carrying the information for autonomous replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):9–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00267207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E., Gralla J. D. Spacer mutations in the lac ps promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1069–1072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M., Nishimura A., Yasuda Y., Hirota Y. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli K-12 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):575–579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Harding N. E., Smith D. W., Zyskind J. W. The chromosomal origin of replication (oriC) of Erwinia carotovora. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2639–2650. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyskind J. W., Deen L. T., Smith D. W. Isolation and mapping of plasmids containing the Salmonella typhimurium origin of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3097–3101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyskind J. W., Smith D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the Salmonella typhimurium origin of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2460–2464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]