Fig. 9.
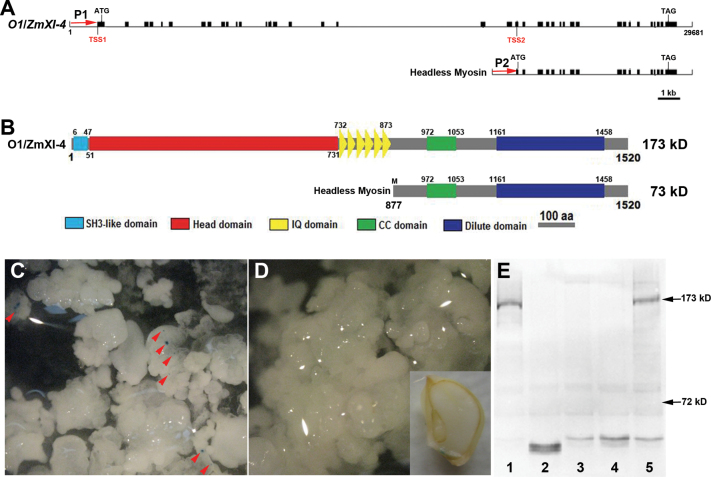
Identification and analysis of the headless derivative of O1. (A) A putative gene model of the maize headless myosin. TSS, transcription start site; P1 and P2, promoter regions of O1 and the headless myosin. (B) Conserved domains present in the maize headless myosin, which lose the N-terminal SH3-like domain, head domain, and IQ motif. (C) GUS staining of the O1pro::GUS construct observed in the maize callus. Red arrowheads indicate the blue signals. (D) No activity is shown for the headless myosin promoter in the callus and developing kernel. (E) Immunoblot analysis of O1 and the headless myosin proteins in developing maize kernels at 20 d after pollination using an antibody described previously (Wang et al., 2012). Lanes: 1, W22 inbred line; 2, o1-ref; 3, o1-N1478A; 4, o1-N1243; 5, the wild type. The arrows on the right indicate the expected protein weights of O1 and the headless myosin proteins. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)