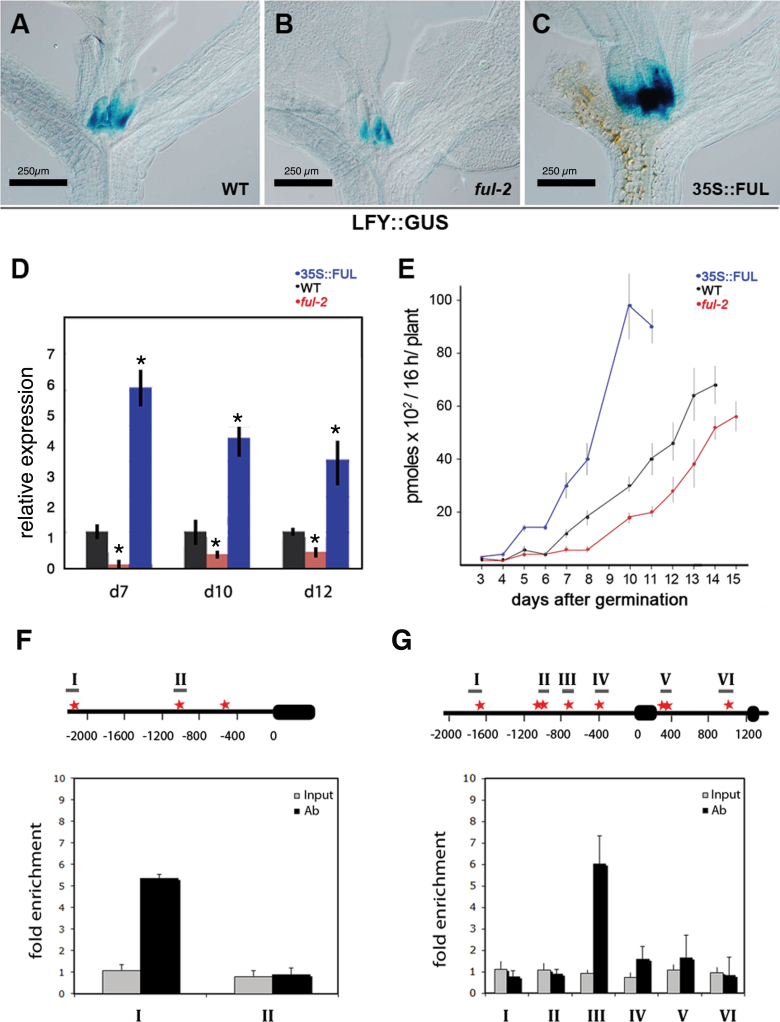
Fig. 2.
FUL regulates key genes in the floral transition process binding directly to SOC1 and LFY promoters. (A–C) Histochemical detection of LFY::GUS activity in the apices of 6-d-old wild type (A), ful-2 (B) or 35S::FUL (C) plants. Scale bars, 250 µm. (D) Relative expression of LFY analysed by qRT-PCR in WT, ful-2, and 35S::FUL plants at 7, 10, and 12 d after germination. The error bars depict the s.e. based on two biological replicates. Asterisks (*) indicate a significant difference (P <0.05) from the WT control according to Student’s t-test. (E) Quantification of LFY:GUS activity in WT, ful-2, and 35S::FUL backgrounds. Plants were grown on plates under long days (LD). At each time point, GUS activity was measured in at least 12 individual apices, and the means ±s.e are given. (F) (Top) Schematic diagram of the LFY upstream promoter region. First exon is represented by a black box, while the upstream genomic region is represented by a black line. The red stars indicate the sites containing either single mismatch or perfect match with the consensus binding sequence (CArG box) of MADS-domain proteins. Amplicons spanning these sites used in the ChIP analyses are represented by grey lines and marked by roman numbers. (Bottom) ChIP enrichment tests showing the binding of FUL-GFP to the LFY-I region. Bars represent the ratio of amplified DNA (35S::FUL:GFP/35S::FUL) in the starting genomic DNA (input) or in the immunoprecipitated DNA with the GFP antibody (Ab). (G) (Top) Schematic diagram of the SOC1 genomic region, including upstream promoter, exons 1 and 2 and the first intron. Exons are represented by black boxes, upstream genomic region and intron by a black line. The red stars mark CArG boxes. Amplicons spanning these sites used in the ChIP analyses are represented by grey lines and marked by roman numbers. (Bottom) ChIP enrichment tests showing the binding of FUL-GFP to the SOC1-III region. Bars represent the ratio of amplified DNA (35S::FUL:GFP/35S::FUL) in the starting genomic DNA (input) or in the immunoprecipitated DNA with the GFP antibody (Ab).