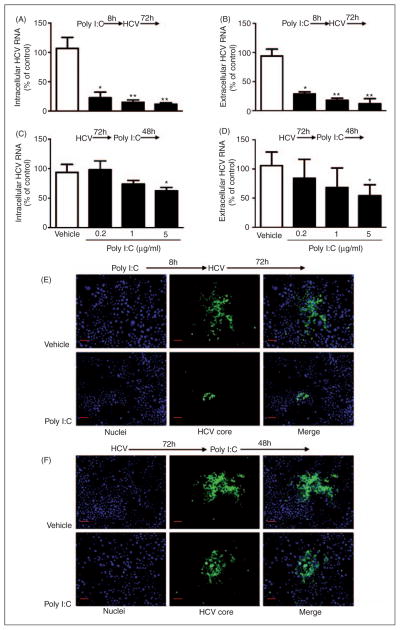
Figure 4.
Effect of poly I:C on HCV replication. (A–D) Effect of Poly I:C on HCV RNA replication. Huh7 cells were stimulated with poly I:C at indicated concentration for 8 h prior to HCV JFH-1 infection (A, B) or stimulated with poly I:C at 72 h post-infection (C, D). Intracellular (A, C) and extracellular (B, D) RNA extracted from Huh7 cells or culture SN was subjected to the real time RT-PCR for HCV and GAPDH RNA quantification. HCV RNA level is expressed as HCV RNA levels relative (%) to the control (vehicle only, which are defined as 100%). The results shown are mean ± SD of triplicate cultures, representative of three experiments (poly I:C-stimulated Huh7 cell vs vehicle-treated cells only: **P<0.01, *P<0.05). (E, F) Effect of poly I:C on HCV core protein expression. Huh7 cells were stimulated with or without poly I:C (1 μg/ml) for 8 h prior to HCV JFH-1 infection (E) or 72 h post-infection for 48 h (F). HCV core protein expression was determined by immunofluorsence staining with Ab against HCV core protein (green). The nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). One representative experiment is shown (original magnification 200×, scale bar: 20 μM).