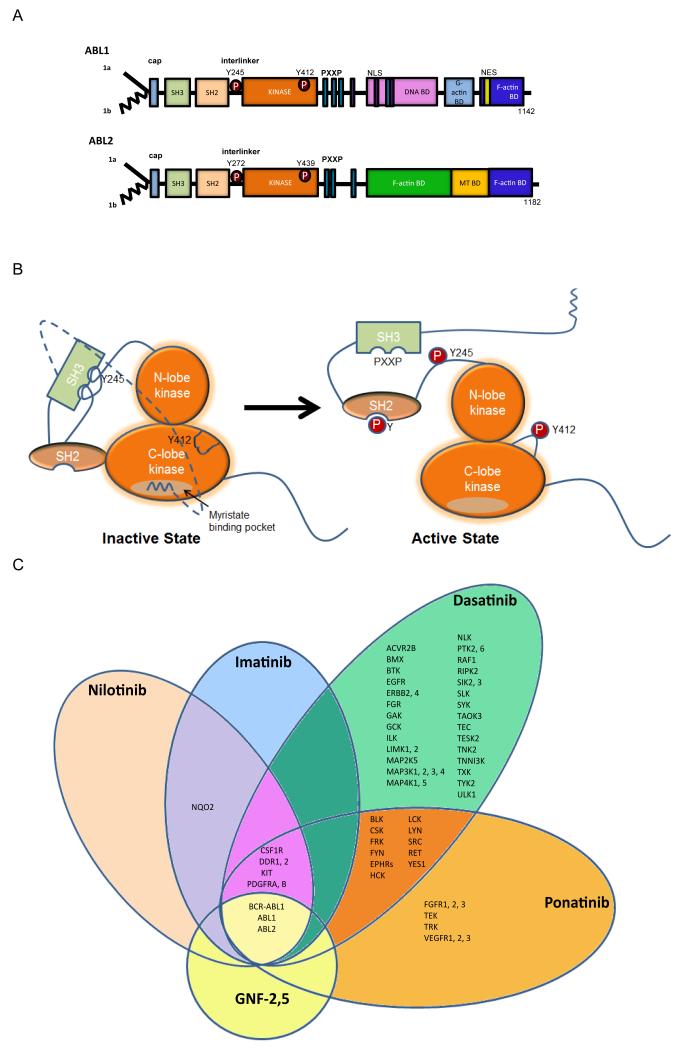
Figure 1. Modular domain structure of ABL family kinases.
A. Schematic representation of the modular domains of the ABL kinases. Alternative splicing of ABL1 and ABL2 produces several isoforms, including 1a isoforms (solid line) and the 1b isoforms (jagged line); the later are targeted for N-terminal myristoylation153. The ABL N-termini are comprised of the Src homology 3 (SH3), SH2 and SH1 domains. The ABL C-termini contain a conserved F-actin-binding domain. ABL1 has a G-actin binding domain whereas ABL2 has a second internal F-actin binding domain. ABL1 has three nuclear localization signal (NLS) motifs and one nuclear export signal (NES) in its C-terminus. Both ABL1 and ABL2 have conserved PXXP motifs to mediate protein-protein interactions. Phosphorylation (P) of ABL1 at Y412 within the activation loop (ABL2 Y439) and Y245 in the SH2-kinase domain linker (ABL2 Y272) stabilizes the active conformation. B. Representation of auto-inhibited (closed) and active (open) ABL kinases to depict the role of intramolecular interactions in the regulation of ABL kinase activity. The SH3 domain binds to the linker sequence connecting the SH2 and kinase domains, while the SH2 domain interacts with C-terminal lobe of the kinase (SH1) domain forming a SH3-SH2 clamp structure. The myristoylated residue in the N-terminus of the 1b ABL isoforms binds to a hydrophobic pocket within the C-lobe of the kinase domain, stabilizing the auto-inhibited conformation. The configuration and interactions of the ABL C-terminal sequences are not included in the model. C. Specificity of selected ABL TKIs: imatinib (Gleevec, STI571; Novartis), nilotinib (Tasigna, AMN107; Novartis), dasatinib (Sprycel, BMS-354825; Bristol-Myers Squibb), ponatinib (Iclusig, AP24534; Ariad Pharmaceuticals) and GNF-2, GNF-5 (allosteric inhibitors in preclinical studies). The kinase selectivity profiles for imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib were generated based on the binding of cellular kinases to inhibitors immobilized on solid support matrices (reviewed previously in 75). Ponatinib-sensitive kinases were identified by in vitro kinase assays; shown are targets with IC50 values of less than 20 nM152. Kinases sensitive to GNF-2 and GNF-5 were identified by in vitro kinase assays56, 154, 155.