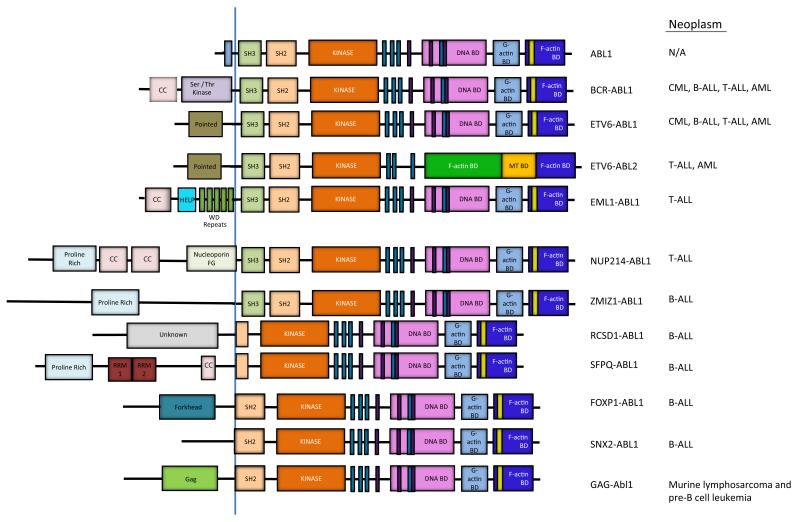
Figure 2. ABL activation by chromosome translocations in leukemia.
Schematic representation of ABL1, and the various ABL1 and ABL2 fusion proteins that arise as a consequence of chromosome translocations in various types of human leukemia. The BCR-ABL1 and ETV6-ABL1 fusions are associated with several types of leukemia including chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), T-cell ALL (T-ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML)58. The ETV6-ABL2 fusion protein is present in rare cases of T-ALL and AML60. The NUP214-ABL1 and EML1-ABL1 fusions are primarily linked to T-ALL, while the RCSD1-ABL1, SFPQ-ABL1, ZMIZ1-ABL1, FOXP1-ABL1 and SNX2-ABL1 fusions are associated with B-ALL57, 59. The coiled-coil (CC) and other motifs in the fusion partner promote oligomerization of the resulting chimeric ABL kinases. The BCR-ABL1, NUP214-ABL1, ETV6-ABL1, ETV6-ABL2, EML1-ABL1, and ZMIZ1-ABL1 fusion proteins retain the SH3, SH2 and SH1 domains of the ABL kinase. The RCSD1-ABL1, SFPQ-ABL1, FOXP1-ABL1 and SNX2-ABL1 fusions lack the SH3 but retain part of or the entire SH2 domain. The v-Abl1 oncoprotein fuses Gag sequences of Abelson murine leukemia virus to sequences upstream of the Abl1 SH2 domain 57, 58. The v-Abl1 oncoprotein induces murine lymphosarcoma and acute pre-B cell leukemia156, 157 (HELP = hydrophobic EMAP-like protein domain, RRM = RNA recognition motif)