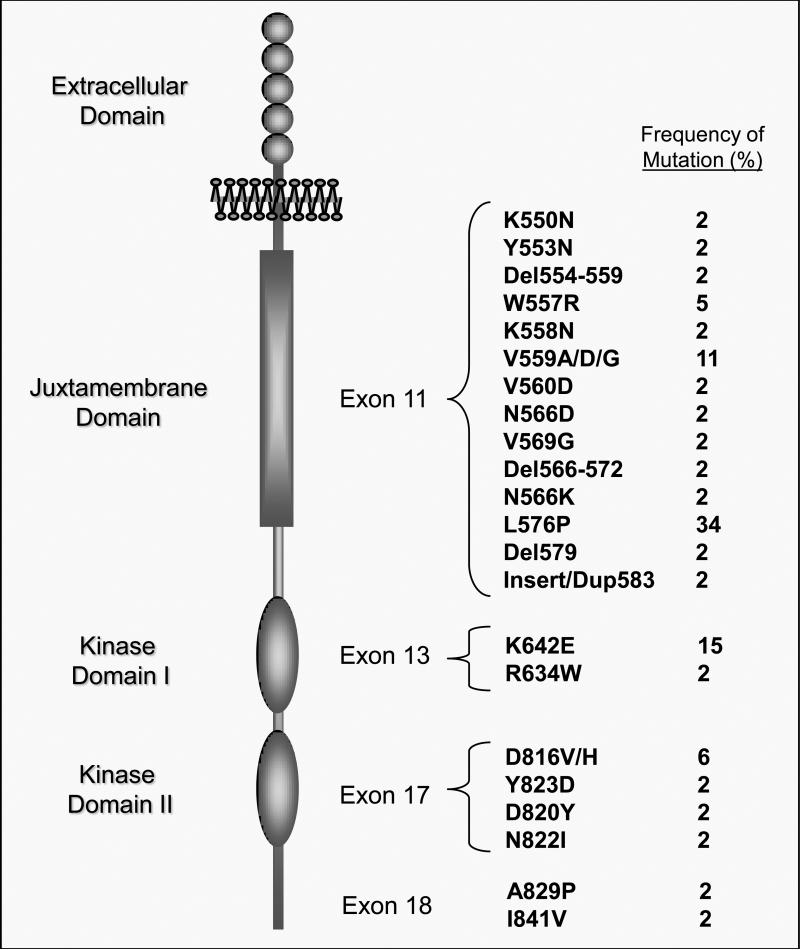
Figure 1.
Schematic Representation of the KIT Tyrosine Kinase Receptor and Mutation Frequency. Five immunoglobulin-like regions (circles) are located in the extracellular domain and serve as the binding site for the KIT ligand, stem cell factor. The juxtamembrane autoinhibitory domain (vertical rectangle) serves to maintain the kinase domains (vertical ovals) in an inhibited state unless the receptor is bound by ligand. KIT mutations occur with highest frequency (~ 70%) in exon 11 of the juxtamembrane domain. Mutations also occur in the kinase domain I, exon 13 (~ 17 %), and kinase domain II, exon 17 (~ 15 %).