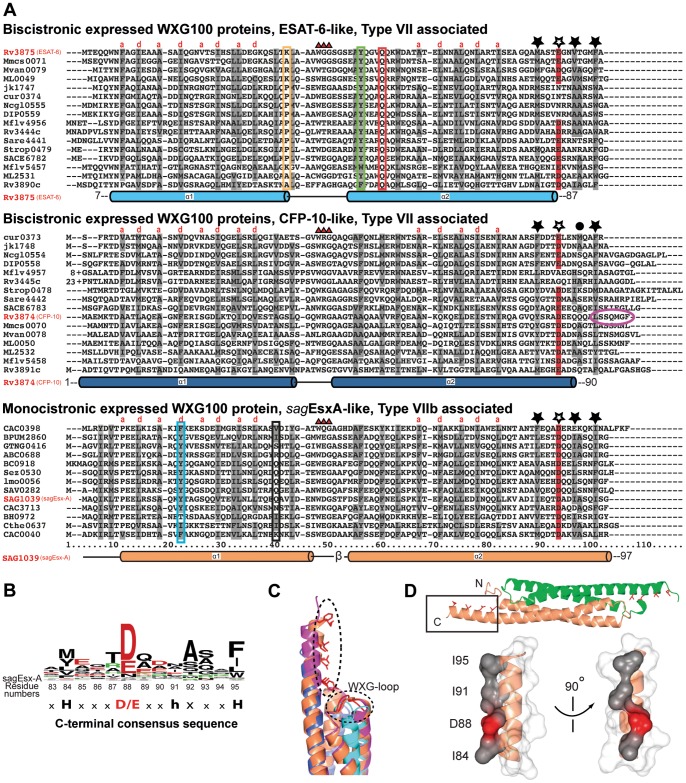
Figure 3. Alignments of the WXG100 subfamilies reveal conserved subfamily specific residues and generally conserved C-terminal residues pattern.
(A) The position of helices, according to the structures of ESAT-6, CFP-10, and sagEsx-A, are shown below the alignments of each subfamily. The four-helix bundle requires mostly hydrophobic residues at the position of ‘a’ and ‘d’ of a helix turn consisting of the heptad helix repeat (a-b-c-d-e-f-g), shown as grey shading on the aligned residues. The key features of ‘ESAT-6-like’ subfamily (top panel): Shown are three highly conserved residues besides the almost invariant WXG motif (marked with red triangles), boxed in K/P38 (yellow), Y51 (green) and Q55 (red). Numbering of residues followed those of ESAT-6 (Rv3875). In the ‘CFP-10-like’ subfamily (middle panel), there are almost no conserved features, except for the C-terminal sequence conservation (marked with asterisks, filled with black for hydrophobic residues and unfilled for acidic residues), shared by all WXG100 superfamily members. In the ‘sagEsx-like’ subfamily (bottom panel), all residues involved in the inter-dimer interactions are hydrophobic except two residues, boxed in cyan and black. The gene IDs of the WXG targets are shown on each line. The numbers correspond to the locus of each genes depicted here. The bacterial species out of the phylum “Actinobacteria” are abbreviated as: Mmcs0071: Mycobacterium sp. MCS, Mvan: M. vanbaalenii, ML: M. leprae, jk: Corynebacterium (C.) jeikeium, cur: C. urealyticum, Ncgl: C. glutamicum, DIP: C. diphtheria, Mflv: M.gilvum, Sare: Salinispora (Sa.) arenicola, Strop: Sa. tropica, SACE: Saccharopolyspora erythraea, and those from the phylum “Firmicutes” as: CAC: Clostridium acetobutylicum, BPUM: Bacillus pumilus, GTNG: Geobacillus thermodenitrificans, ABC: alkaliphilic Bacillus clausii, BC: Bacillus cereus, Sez: Streptococcus equi, Lmo: Listeria monocytogenes serovar, SAV: Staphylococcus aureus, SAG: Streptococcus agalactiae, BH: Bacillus halodurans, Cthe: Clostridium thermocellum, respectively. (B) The C-terminal consensus sequence HxxxD/ExxhxxxH is shown as a sequence logo diagram. The residue at the eighth position is marked with ‘h’ indicating lower conservation on hydrophobic residues (see panel A). (C) Structural superposition of CFP-10 (blue), ESAT-6 (cyan), sagEsxA (orange) and sauEsxA (violet): Only the C-terminal helices along with the adjacent WXG loops facing towards helices are shown. For better visibility only the side chains of sagEsxA are shown. (D) The side chains of the conserved C-terminal residues decorate the same side of the C-terminal helix as observed in the structures of the WXG100 proteins, shown is that of sagEsxA (see text), marked with asterisks in panel A. To emphasize the structural feature, the C-terminal helix is shown in a surface representation, where the consensus hydrophobic residues are in grey and the acid residue is in red. The remaining residues (x) are shown in light grey.