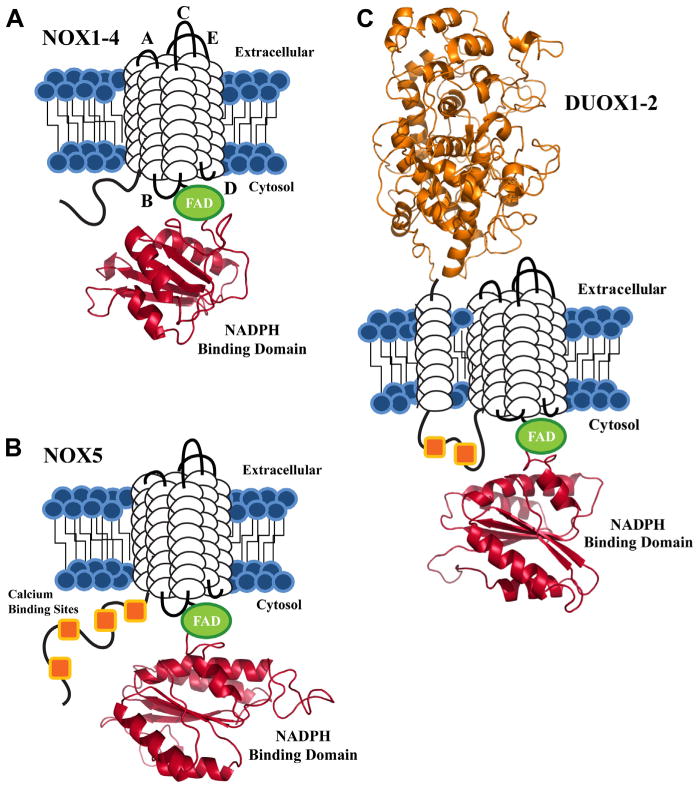
Fig. 1.
Schematic view of the conserved structural features of the NADPH oxidase proteins. Each isoform contains 6 putative TM domains (white cylindrical loops), with C-terminal FAD (green) and NADPH binding domains (red). The NADPH binding domain structural models were created by the SWISS-MODEL program server with hNOX2 (PDB: 3A1F) as the template, visualized by Pymol software. (A) NOX1-4 are depicted with loop regions labeled based on established designations: extracellular loops A, C, E and intracellular loops B and D. (B) The NOX5 isoform shares the same structural motif as NOX1-4, with a novel N-terminal calcium binding region, composed of 4 EF-hand calcium binding sites (orange squares). (C) DUOX1-2 are unique to the NADPH oxidase family, as both isoforms contain an extracellular N-terminal peroxidase homology domain (orange) and two cytosolic calcium binding sites.