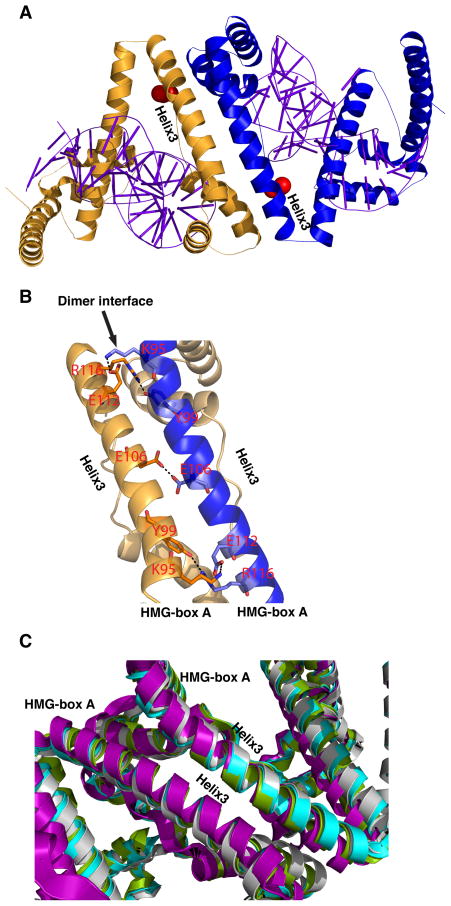
Figure 4. Dimerization interface.
(A) Overview of two molecules of TFAM forming a dimer in the TFAM/HSP1crystal structure. Each TFAM molecule is bound to its own DNA fragment. Helix 3 from one HMG-box A domain forms an antiparallel interface with the corresponding helix 3 from another molecule. The locations of the cysteines used for protein labeling are indicated in red. (B) Close-up of the antiparallel dimerization interface. Residues involved in hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are labeled. (C) Superimposition of the dimerization interfaces from all four TFAM/DNA structures: TFAM/LSP-28 bp (green, pdb:3TMM), TFAM/LSP-22 bp (cyan, pdb:3TQ6), TFAM/HSP1-22 bp (purple), and TFAM/nonspecific DNA-22 bp (grey). RMSD values relative to TFAM/LSP-22bp are as follows: TFAM/LSP-28 bp, 0.887; TFAM/HSP1-22 bp, 1.056; TFAM/nonspecific DNA-22 bp, 0.951.