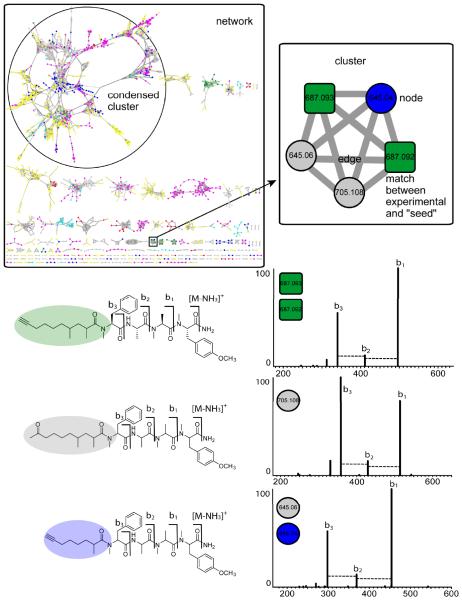
Figure 2. Validation of nodes and annotation of MS/MS spectra.
Using the carmabin A “seed” as a starting node, molecular networking revealed that carmabin A was present in two different cyanobacterial collections (also in Figure 3). In the same cluster, there were three additional nodes of two precursor masses, m/z 645.0 and 705.1. Putative assignment of modifications based on the precursor mass difference – sodium, potassium, alkylated, halogenated, oxidized, etc. – and mass differences between peaks in the MS/MS spectra also provide insight to the structures of the related NPs. Manual inspection of the carmabin A MS/MS spectrum showed a sequence tag consistent with b-type ions. Inspection of the MS/MS spectra of the connected nodes, m/z 645.0 and 705.1, matched to known lipopeptides in the same molecular family as carmabin A, but with differing lengths and degrees of unsaturation of the lipophilic tail. With one seed, carmabin A, molecular networking was able to dereplicate carmabin A and two MS/MS spectra that match to the structurally related analogs, carmabin B and dragomabin.