Figure 5.
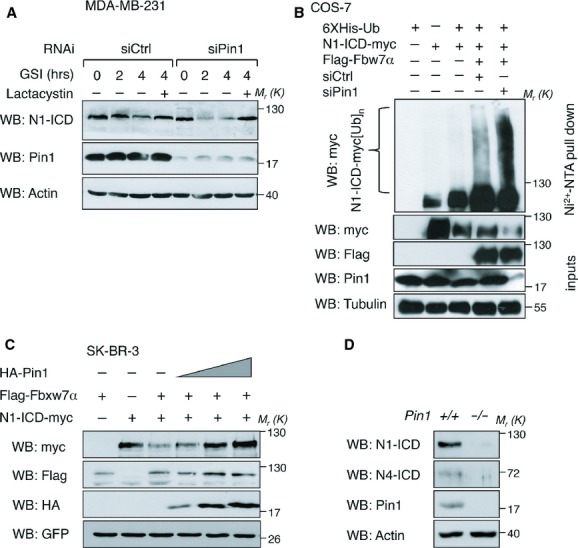
Pin1 rescues N1- and N4-ICD from Fbxw7α-mediated proteasome-dependent degradation. Molecular weights (Mr) are indicated in kDa.
A Pin1 knockdown accelerates the decay of endogenous N1-ICD. Western blot of endogenous N1-ICD following RNA interference (RNAi) with the indicated siRNAs and time points following GSI or GSI plus Lactacystin (+) chase is shown.
B Pin1 depletion enhances Fbxw7α-dependent poly-ubiquitination of N1-ICD. Western blot analysis of high molecular weight N1-ICD-myc products (N1-ICD-myc[Ub]n) from a Ni-NTA pull-down in COS-7 cells transfected with the indicated vectors along with control- or Pin1 siRNA. Input levels of over-expressed proteins are shown.
C Pin1 overexpression rescues N1-ICD levels in presence of Fbxw7α. Western blot analysis of lysates from SK-BR-3 cells over-expressing N1-ICD-myc, Flag-Fbxw7α along with empty (–) or increasing amounts of HA-Pin1 expressing vector, normalized for co-expressed GFP protein.
D Pin1−/− mammary epithelial cells have impaired Notch pathway activation. Western blot analyses of primary MECs from indicated female mice.
