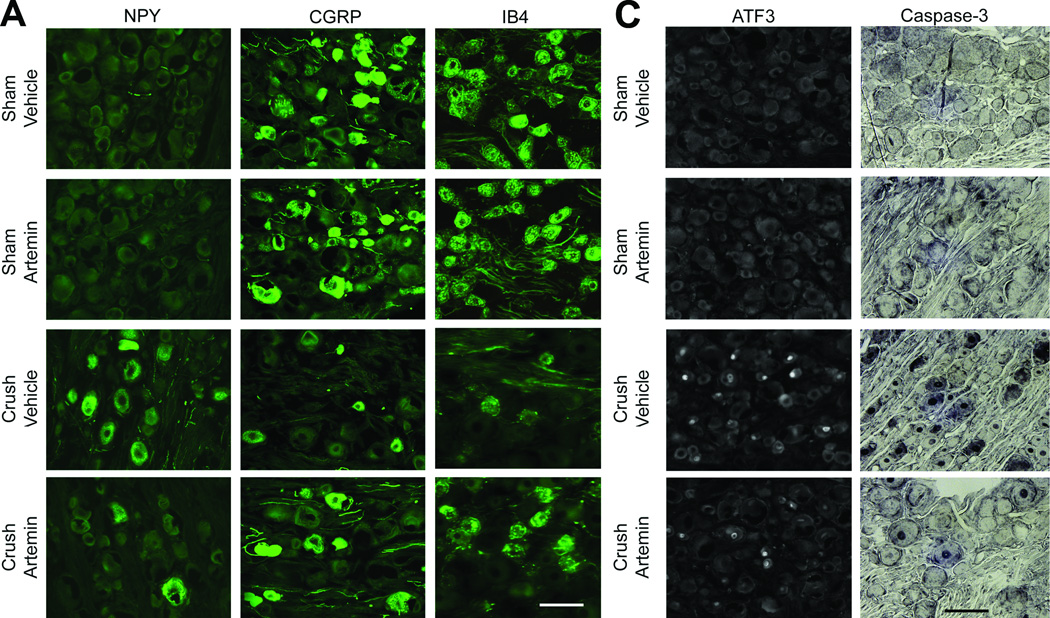
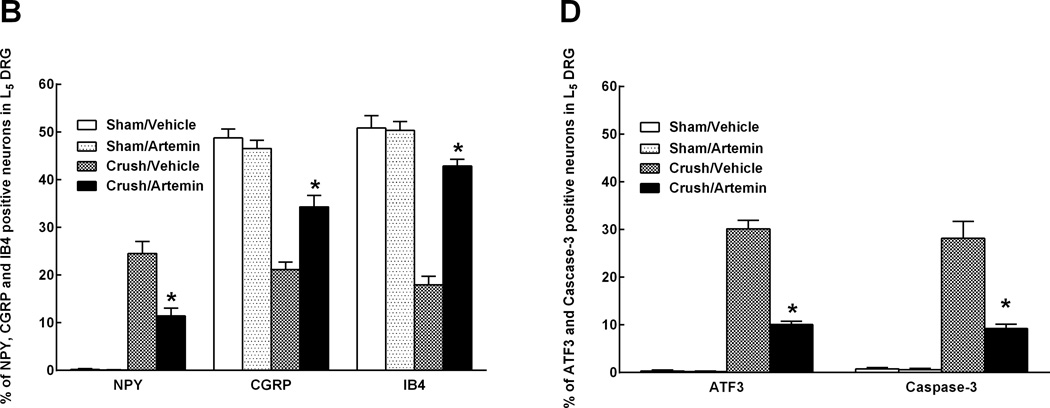
Figure 3.
Artemin blocks neurochemical signs in the DRG of nerve crush-induced neuropathy 6 weeks following injury. A. Nerve crush resulted in increased NPY labeling and decreased CGRP as well as IB4 labeling within the ipsilateral L5 DRG. Artemin attenuated the nerve-crush induced increase in NPY and the decreased CGRP and IB4 labeling. B. The graph shows quantification of NPY, CGRP and IB4 labeled neuronal profiles in the ipsilateral L5 DRG. The counts confirm that artemin ameliorated the nerve-crush induced increase in NPY and the decreased CGRP and IB4 labeling. Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) compared to vehicle treatment after nerve crush. C. Nerve crush induced ATF3 labeled neuronal profiles were markedly reduced with artemin treatment. A similar decrease in nerve-crush induced caspase-3 labeled neuronal profiles was observed in artemin treated rats. Scale bar indicates 50 µm for all images. D. The graph shows quantification of ATF3 and caspase-3 labeled neuronal nuclei from counted sections confirming that artemin decreased the percentage of ATF3 and caspase-3 labeled neurons following nerve crush. Asterisks indicates significant differences (P < 0.05) compared to vehicle treatment after nerve crush.