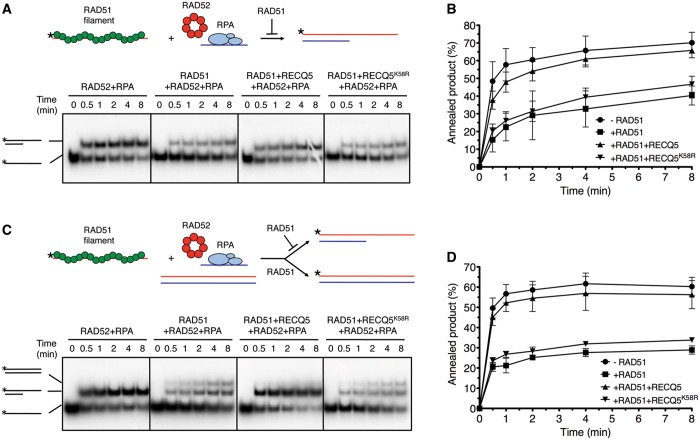
Figure 3.
RECQ5 helicase counteracts the inhibitory effect of RAD51 on RAD52-mediated ssDNA annealing in vitro. (A) Upper panel: reaction scheme depicting the effect of RAD51 (green circles) on annealing of two complementary oligonucleotides (59-mer and 30-mer represented by red and blue lines, respectively) in presence of RAD52 and RPA. RAD52 is depicted as a heptameric ring structure (red circles). The 30-mer oligonucleotide can accommodate binding of one RPA heterotrimer (light blue ovals). Lower panel: all reactions were carried out at 30°C in buffer R supplemented with ATP-regenerating system. Reactions contained 5′ end radiolabeled 59-mer oligonucleotide (2.5 nM), either free or pre-coated with RAD51K133R (100 nM), a 30-mer oligonucleotide (2.5 nM) complementary to the 5′-half of the 59-mer, RAD52 (60 nM) and RPA (30 nM). Where indicated, RECQ5 or RECQ5K58R were present at a concentration of 80 nM. Reaction aliquots at indicated time points were subjected to PAGE followed by phosphorimaging as described in ‘Materials and Methods’. (B) Quantification of data shown in (A). Each data point represents the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation. (C) Upper panel: reaction scheme depicting the effect of RAD51 on annealing of two complementary oligonucleotides in presence of a homologous duplex, RAD52 and RPA. RAD51 filament formed on the radiolabeled oligonucleotide (red line with asterisk) inhibits RAD52/RPA-mediated annealing and promotes strand exchange with the homologous duplex. Lower panel: reactions were carried out and analyzed as in (B). Homologous 59-mer duplex was present at a concentration of 2.5 nM. Schemes of radiolabeled DNA species are shown on left. Radioactive label at the 5′ end is depicted by asterisks. (D) Quantification of data shown in (C). Each data point represents the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation.