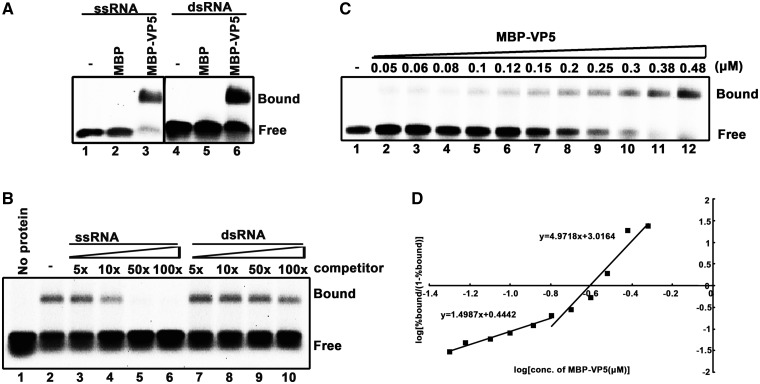
Figure 2.
VP5 binds to RNA in a cooperative manner. (A) A gel mobility shift assay was performed to evaluate the dsRNA or ssRNA binding capacity of MBP-VP5. Ten picomoles MBP-VP5 was incubated with 0.1 pmol HEX-labeled ssRNA (RNA1) or dsRNA (RNA1/RNA2) substrate for 30 min. Lanes 1 and 4, no protein supplemented; lanes 2 and 5, 10 pmol MBP supplemented; lanes 3 and 6, 10 pmol MBP-VP5 supplemented. Protein-bound and free RNA strands are indicated. (B) 0.1 pmol HEX-labeled ssRNA probe and 2 pmol MBP-VP5 were incubated with unlabeled competitor ssRNA or dsRNA at the indicated increasing concentrations (in 5-, 10-, 50-, 100-folded excess over the amount of HEX-labeled ssRNA). The bound complexes were analyzed in a gel mobility shift assay. (C) Gel mobility shift assays were performed by incubating the indicated increasing concentrations (0.05–0.45 μM) of MBP-VP5 with 0.1 pmol RNA1 probe. (D) The RNA binding data in (C) were quantified, and a Hill transformation was applied. The Hill coefficients of the RNA binding of VP5 at low and high protein concentrations are indicated.