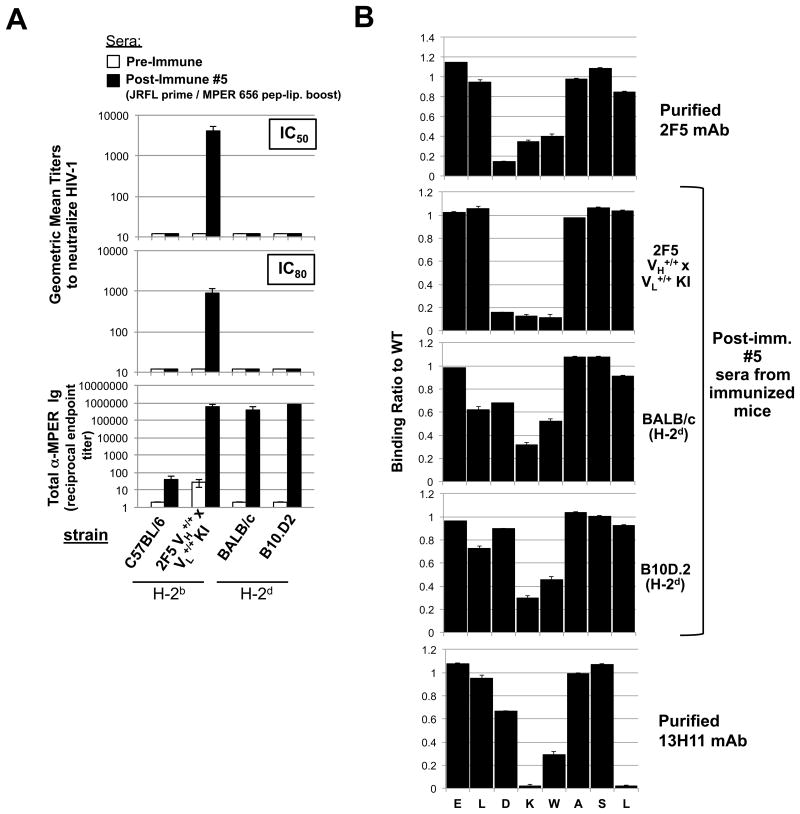
Figure 5. Neutralization activity and MPER epitope specificity of MHC-restricted MPER+ serum Ab responses elicited by vaccination.
A. Serum neutralizing Ab induction in immunized “high responder” (H-2d) congenic B10 and BALB strains was measured at peak MPER+ serum Ig induction (10d after 5th immunizations with experimental (JRFL prime/TLR4/9-MPER peptide-liposome boost) regimen, or as a negative control in pre-immune sera, using the HIV-1 B.MN.3 isolate in the TZM-b/l neutralization assay (28,53). Shown are GMTs of reciprocal dilutions of sera to inhibit HIV-1 B.MN.3 at 50 or 80% levels (top panels) and corresponding MPER (2F5)-specific Ig levels (calculated and represented as in Fig. 1B-C as reciprocal endpoint titer means±SEMs (bottom panel). Data shown uses sera taken from >3 mice/group assayed. For comparison, also shown as controls are the (H-2b) “low-responder” C57BL/6 strain and 2F5 complete KI mice (on the C57BL/6 background). B. SPR epitope mapping of serum taken from immunized “high responder” (H-2d) congenic B10.D2 and BALB/c strains, measured at peak MPER+ serum Ig induction (10d after 5th immunizations with experimental regimen). Shown are SPR sensograms of serum Ab binding to WT or mutant alanine scanning SP62 (2F5 epitope-containing) peptides, represented as normalized binding i.e., ratio between binding responses of sera to the alanine scanning mutant and WT SP62 peptides. As controls for specificity to the 2F5 neutralizing core DKW, also shown are binding profiles of 10 μg/ml purified mAbs 2F5 and 13H11 (upper and lower panels, respectively). All serum Ab binding data shown is representative of measurements of individual samples repeated in two independent experiments using >2 mice/group assayed.