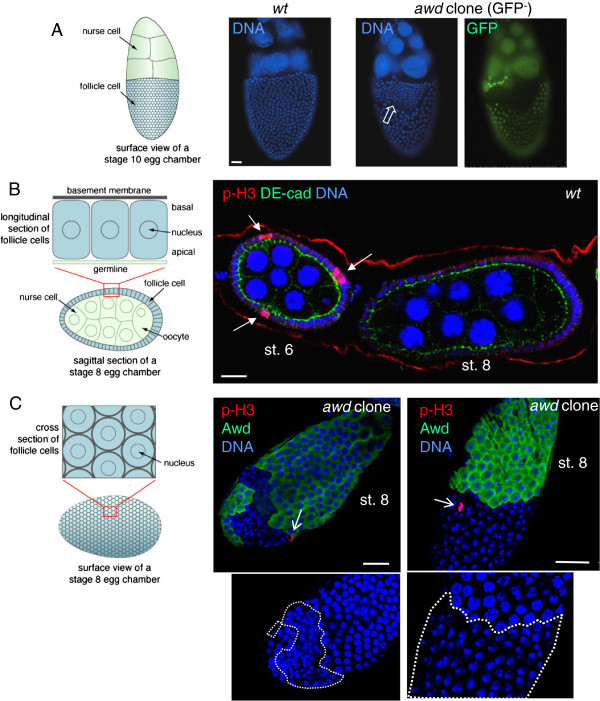
Figure 1.
Dysregulated proliferation in awd mutant follicle cells. (A-B) Control egg chambers were dissected from yw (representing wild-type) females. Egg chambers containing awd clones (no GFP) were dissected from hs-flp; +/+; Ubi-GFP, FRT82B/FRT82B, awdj2A4 females. (A) In follicular epithelium, awd mutant clones show more numerous but smaller nuclei (empty block arrow) in comparison with the adjacent normal follicle cells and with yw egg chambers (left). To visualize nuclei the stage 10 egg chambers were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) yw egg chambers were stained for p-H3 (red), DE-cadherin (green) and DNA (blue). p-H3 detects mitotic cells only in pre-stage 7 eggs (arrows). (C) Egg chambers containing awd clones were dissected from yw; en2.4-Gal4e22c, UAS-flp/+; FRT82B/FRT82B, awdj2A4, and stained for p-H3 (red), Awd (green) and DNA (blue). In awd mutant clones (lack of Awd expression), p-H3 positive cells can be detected post-stage 6 (sharp arrows). Duplicate images showing only nuclear staining (insets) highlight the smaller nuclei in awd mutant clones (dashed lines). Schematic representations of the positioning and viewing of follicle cells in the egg chamber are shown in the left side of A, B and C. Bars are 20 μm. DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; p-H3, phosphorylated histone H3.