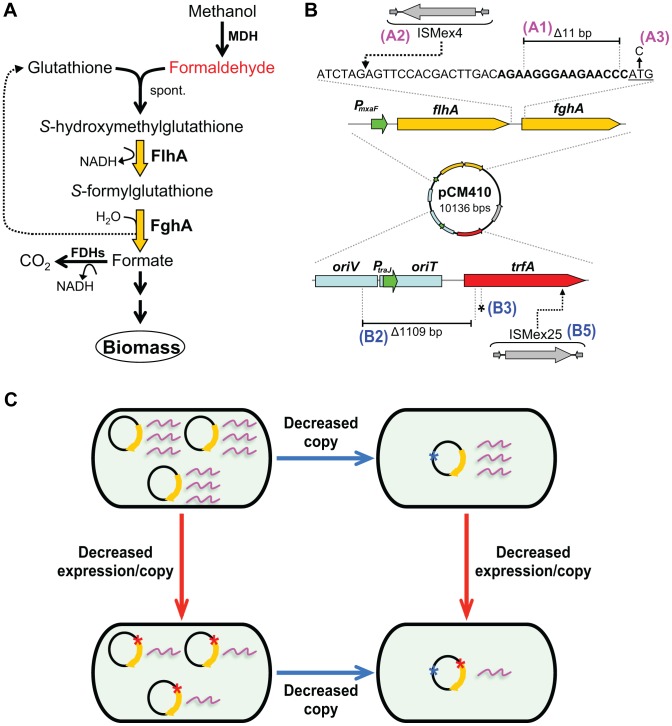
Figure 1. Adaptive mutations that optimized the expression of the GSH-linked pathway.
A) The GSH-linked formaldehyde oxidation pathway in the EM strain. The enzymes of the GSH-linked pathway are indicated with yellow arrows. MDH, methanol dehydrogenase; spont., spontaneous reaction of formaldehyde and GSH; FlhA, S-hydroxymethyl GSH dehydrogenase; FghA, S-formyl-GSH hydrolase; FDHs, formate dehydrogenases. B) Adaptive mutations identified on the introduced plasmid (pCM410) expressing the introduced formaldehyde pathway. Mutations occurring in the predicted ribosome-binding site (bold text) of fghA, or its upstream region are shown in magenta (Class A). Mutations occurring in regions that control plasmid replication are shown in blue (Class B). The fghA start codon is underlined. trfA, a gene encoding the TrfA protein essential to plasmid replication; PmxaF, promoter of the flhA-fghA gene cassette; oriV, origin of replication recognized by the TrfA protein; oriT, origin of transfer. ISMex4 and ISMex25, two insertion sequences native to M. extorquens AM1. C) Diagram of orthogonal mechanisms of Class A and B mutations on gene expression.