Figure 1.
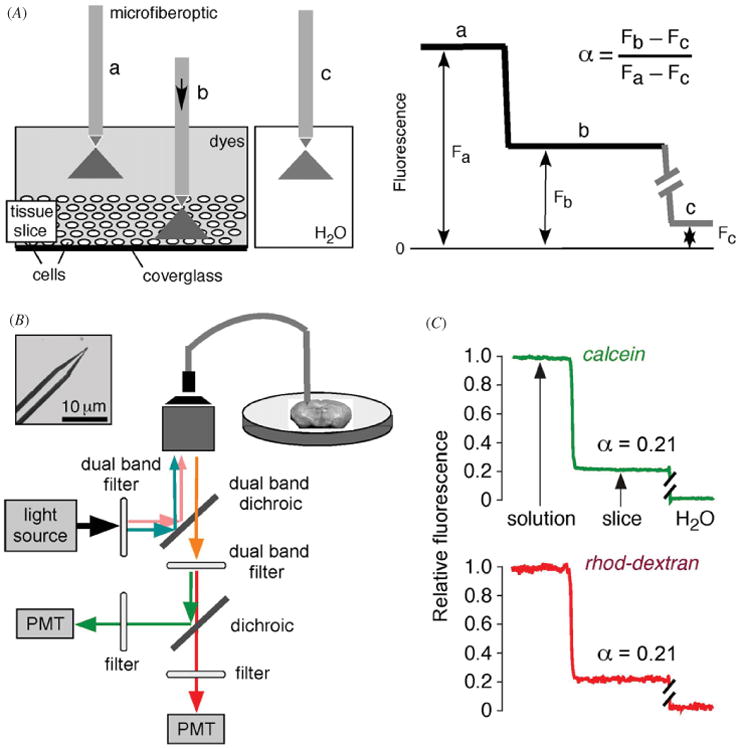
Extracellular space volume determination by fluorescent dye partitioning with microfiberoptic detection (DPMD). Left: method principle, showing microfiberoptic detection of fluorescence of a non-interacting, aqueous-phase dye in tissue slice and overlying solution. The illumination/detection volume is approximately conical, with most of the light collected from near the fiberoptic tip. Right: schematic of data, showing α determination from the ratio of (background-subtracted) dye fluorescence in slice to that in overlying solution. (B) Instrumentation showing multi-mode etched microfiberoptic with micron-size tip inserted into the overlying solution and tissue slice. Inset shows microfiberoptic tip geometry. Fluorescence from two probes of different colors are detected simultaneously using photomultipliers. (C) ECS volume measurement in mouse brain slice with microfiberoptic tip positioned at depth 200 μm in a 400 μm-thick brain slice. Adapted from [17].
