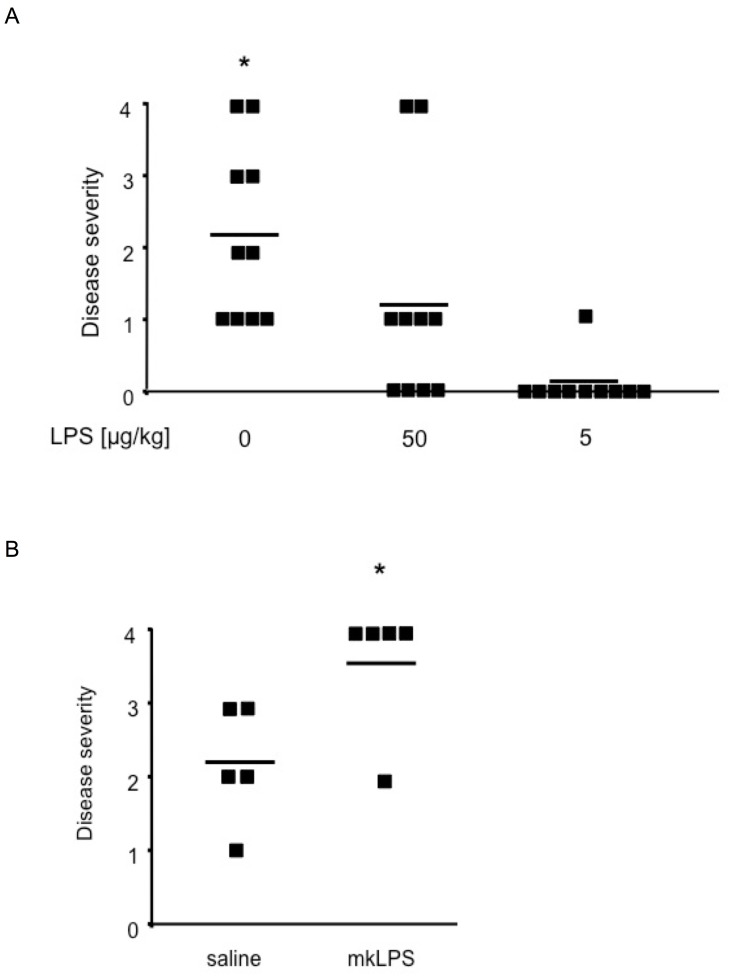
Figure 2. TLR4 signaling is crucial for prevalence and severity of experimental autoimmune myocarditis.
(A) Systemic administration of low dose LPS curbed the induction of experimental autoimmune heart disease. Wild type BALB/c mice treated with low doses LPS developed myocarditis with significantly reduced severity and prevalence compared to saline treated controls. Mice were immunized with M7Aα peptide in CFA and treated by intraperitoneal injection 3 times, on days 5, 9, and 13 after the initial immunization, with the indicated doses of highly pure LPS or saline. Squares represent individual mice, lines indicate mean values. * p<0.05 when compared to other groups using ANOVA for multiple-sample comparisons (Bonferroni). (B) Antagonizing the LPS receptor TLR4 significantly increased severity of autoimmune myocarditis. mkLPS, which lacks the myristoyl fatty acid moiety of lipid A, antagonized TLR4 signaling through direct interaction with TLR4. Mice immunized with M7Aα peptide in CFA and mkLPS developed significantly more severe myocarditis than control mice receiving M7Aα peptide in CFA and saline. Disease severity was determined by histopathology 21 days after the initial immunization. Squares represent individual mice, lines indicate mean values. * p<0.05 by Student;s t-test. One representative result out of 4 independent experiments is shown.