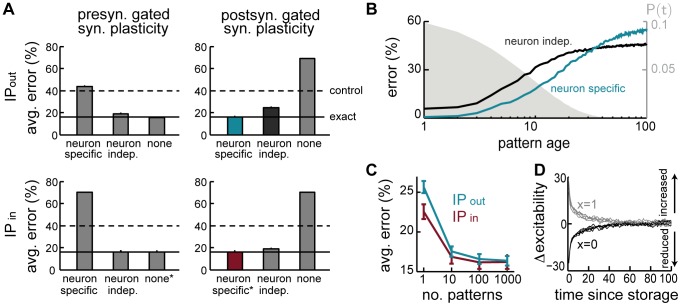
Figure 4. Intrinsic plasticity.
A. Effects of different forms of IP (rows) for different forms of synaptic plasticity (columns). Recall performance is shown for different variants of each form of IP (bars), entailing different approximations of the exact (optimal) dynamics. Dashed lines show control performance of an optimized feedforward network, as in Fig. 2C–E; solid lines show performance of exact dynamics, asterisks mark neural dynamics that are formally equivalent to the exact case. B. Recall performance as a function of pattern age with neuron-independent (black) and -specific (blue) variants of 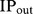 for the postsynaptically-gated learning rule. Gray filled curve shows distribution of pattern age. C. Recall performance for an online implementation of the two forms of IP. D. Net change in excitability induced by the two forms of IP together as a function of time since memory storage for neurons that were either active (gray) or inactive (black) in the originally stored pattern. Lines correspond to different random sequences of consecutively stored patterns.
for the postsynaptically-gated learning rule. Gray filled curve shows distribution of pattern age. C. Recall performance for an online implementation of the two forms of IP. D. Net change in excitability induced by the two forms of IP together as a function of time since memory storage for neurons that were either active (gray) or inactive (black) in the originally stored pattern. Lines correspond to different random sequences of consecutively stored patterns.