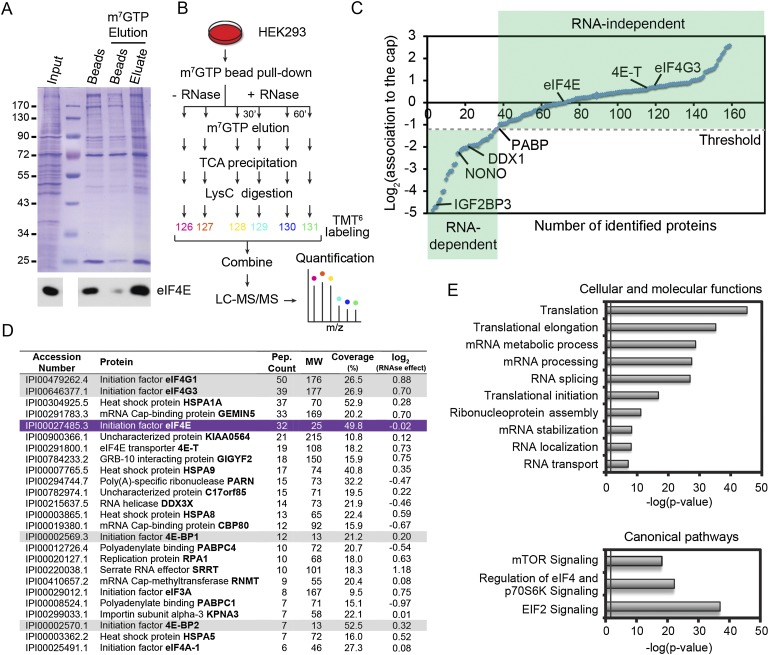
Figure 1.
Global quantitative assessment of proteins that associate with the mRNA 5′ cap. (A) Enrichment of eIF4E (immunoblot in the bottom panel) and associated factors after specific elution with m7GTP (Coomassie gel; fifth lane). (B) Schematic diagram of the multiplex work flow developed for identification and quantitation of the 5′ cap-binding complex by combining m7GTP pull-down and TMT6 labeling in the presence or absence of RNase/Benzonase for 30 or 60 min. (C) Distribution of ∼160 proteins found to be associated to the 5′ cap-binding complex. The RNase dependence ratios (treated/untreated) are plotted on a log2 scale, normalized with respect to eIF4E abundance. Proteins with a log2 ratio ≤1.3 (PABPC1 threshold), such as DDX1, NONO, and IGF2BP3, were considered RNA-dependent. (D) List of the most abundant associated proteins ranked according to the numbers of peptides identified. Gray shading indicates proteins previously shown to interact directly with eIF4E (purple). Accession numbers are from the International Protein Index (IPI). (E) Classification of RNA-insensitive candidates according to cellular and molecular functions or canonical signaling pathways using the DAVID bioinformatics database (http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov) or the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis platform (IPA; http://www.ingenuity.com) according to adjusted P-value. The gray line indicates minimum threshold (P = 0.05).