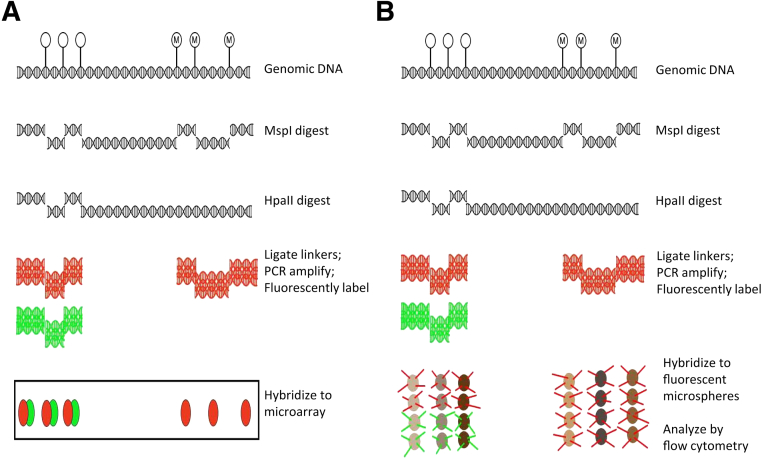
Figure 1.
A: Schematic of the HELP assay. Genomic DNA is digested with either MspI (methylation insensitive) or HpaII (methylation sensitive). The resulting fragments are ligated to linkers and PCR amplified with linker-specific primers. Amplicons are fluorescently labeled (as shown, red for amplicons from MspI-digested genomic DNA and green for HpaII-digested genomic DNA) and hybridized to oligonucleotide microarrays. Only relatively short fragments are amplified by Taq polymerase. Regions of relative hypomethylation will show signal from both MspI- and HpaII-digested DNA, whereas regions of relative hypermethylation will show a predominance of MspI signal. B: MELP modification of HELP assay. Rather than hybridizing to oligonucleotide arrays, amplicons (with red and green denoting the initial MspI and HpaII digests, respectively) are hybridized to oligonucleotides covalently linked to fluorescent microspheres with distinct fluorescent properties (depicted as shades of brown). The microspheres are subjected to flow cytometry and analyzed for locus/microsphere identity (determined by brown intensity) and for amplicon amount (determined by red/green intensity).