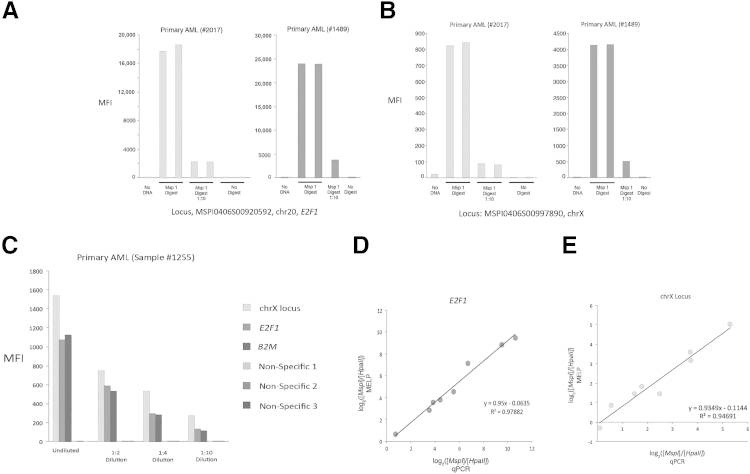
Figure 2.
The MELP assay is both quantitative and specific. A and B: Linker-mediated amplification of MspI-digested DNA was performed. Amplicons were hybridized to fluorescent microspheres and detected by branched DNA hybridization. A 1:10 dilution of amplicons is also assayed. Results are shown for two independent primary AML samples at E2F1 (A) and an unnamed locus on chromosome X (B), both of which are in the HELP-defined methylation classifier for AML. C: A similar assay to A and B was performed, but input DNA was diluted 1:2, 1:4, and 1:10, rather than amplicon dilution, as in A and B. Results are shown for the two loci in A and B and for B2M. In addition, fluorescent microspheres coupled to nonspecific oligonucleotides were included to determine background signal. D and E: Relative amplicon quantitation by MELP compared with quantitation by PCR. MELP was performed on primary AML samples, and signal ratio from MspI and HpaII digests of E2F1 (D) and an unnamed locus on chromosome X (E) were normalized to ratios of the hypomethylated locus, B2M. Amplicon quantitation was also determined by locus-specific qPCR. MFI, mean fluorescent intensity.