FIGURE 3.
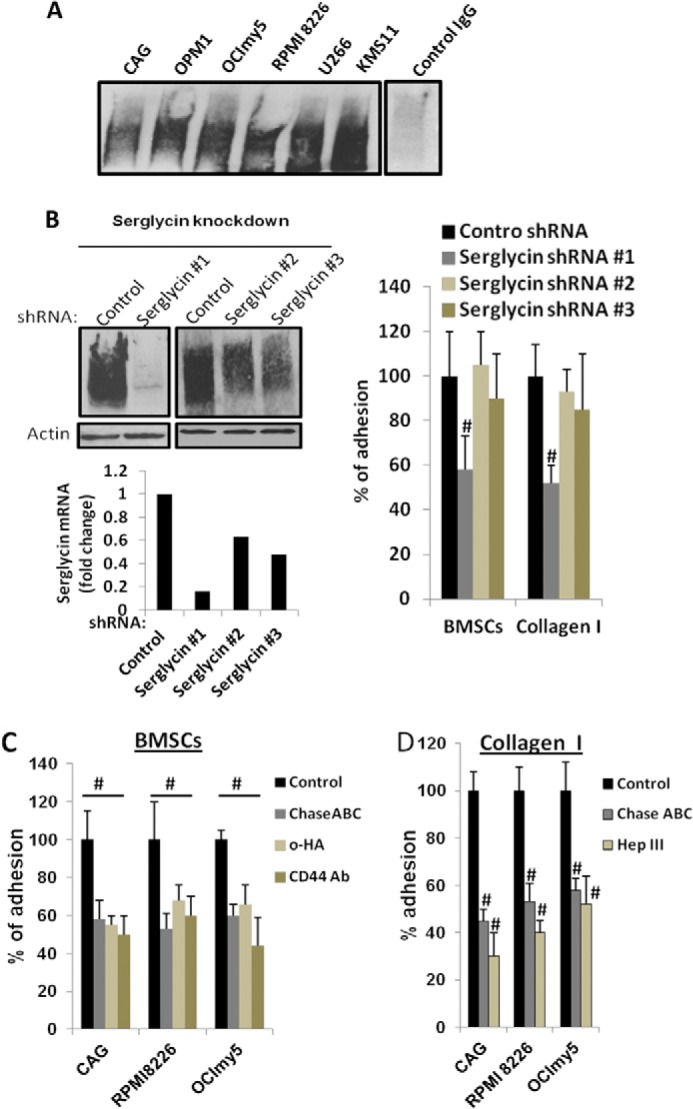
Serglycin promotes myeloma cell adhesion to bone marrow stromal cells and collagen I. A, serglycin secreted by myeloma cells binds to CD44. Recombinant soluble CD44 (CD44-IgG1) was added to the culture supernatants from 6 different human myeloma cell lines. After 8 h of incubation at 37 °C, CD44-IgG was precipitated using protein G-Sepharose beads and subjected to Western blotting for serglycin. Serglycin was not precipitated using control human IgG. B, CAG cells were infected with lentiviral vectors coding for control or serglycin shRNA. Left upper panel: Western blotting of cell extracts of stably infected cells demonstrates effective knockdown of serglycin expression using serglycin shRNA# 1 and partial knockdowns using serglycin shRNAs #2 and #3. Left lower panel: mRNA expression of serglycin assessed by real time PCR. Right panel: myeloma cells after serglycin knockdown adhere less to bone marrow stromal cell (BMSC) line HS-5 and collagen I. Control or serglycin-knockdown CAG cells were seeded to plates that were pre-coated with either BMSC HS-5 or collagen I. After 2 h, non-adherent cells were removed, and percentage of adherent cells were determined as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Values were normalized to control, which is arbitrarily set at 100% (mean ± S.D. of triplicates from three independent experiments). #, p < 0.05 compared with control. CAG cells with partial knockdowns for serglycin adhered to a similar extent to control cells. C, adhesion of myeloma cell lines (CAG, RPMI 8226, and OCImy5) to BMSCs was reduced significantly in the presence of CD44 antagonists. Calcein-labeled myeloma cell lines were added to BMSC HS-5 coated 96-well plates in the presence or absence of CD44 antagonists: small hyaluronan oligosaccharides (o-HA) (100 μg/ml) or adhesion blocking CD44 antibody (hermes-1). To determine the role of CS chains in cell adhesion, myeloma cells were also pretreated with Chase ABC enzyme prior to the addition to HS-5 coated wells. After 2 h, unbound cells were removed and adherence of myeloma cells was determined using a fluorescence plate reader. Data are expressed as percentage control from three different experiments. #, p < 0.05 compared with control. D, myeloma cells (CAG, RPMI 8226, and OCImy5) pre-treated or untreated either with Chase ABC enzyme or Hep III enzyme, were allowed to adhere to collagen I-coated plates for 2 h. Unbound cells were then removed, and adherent cells were then fixed and stained with 0.25% crystal violet. Cells were then lysed and absorbance read at 590 nm. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. of triplicates from three separate experiments. #, p < 0.05 compared with control.
