FIGURE 1.
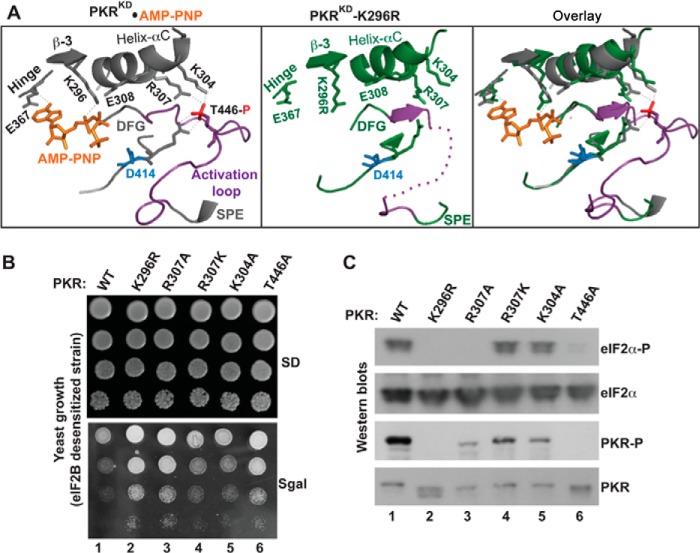
Functional coupling between the phosphorylated activation loop and the helix-αC. A, analyses of PKR KD structures. The structural coordinates of PKR-KD-K296R (PDB ID: 3UIU) and PKR- KD bound to AMP-PNP and eIF2α (PDB ID: 2A19) were aligned in a single PyMol file by pairwise alignment. Proteins of the PKR-KD (gray) and the PKR-KD-K296R (green) are represented as ribbons. For clarity, the entire structure of eIF2α and several structural elements in PKR are omitted. The conserved residues at the helix-αC (E308, R307, and K304), β-strand 3 (β-3, K296), hinge (E367), activation loop (T446), and catalytic loop (R413 and D414) are shown. The activation loop (region between the DFG and SPE motifs) is colored in purple. The phosphate moiety (red) of the phosphorylated Thr-446 salt-bridges (thin dotted line in gray) with the residue Arg-413 from the catalytic loop and residues Lys-304 and Arg-307 from the helix-αC. The thick purple dotted line in the PKR-KD-K296R structure represents the unresolved portion of the activation loop. The K296R mutation is shaded yellow. B, in vivo analysis of PKR mutants by growth in yeast. The yeast strain H17 (eIF2B-desensitive) expressing WT PKR or indicated mutants were serially diluted and spotted on SD and SGal media. The Slg− phenotype on SGal medium indicates the functionality of PKR alleles. C, in vivo analysis of PKR and eIF2α phosphorylation. Whole cell extracts were prepared from yeast cells indicated in B and subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies of phosphorylated eIF2α (eIF2α∼P), eIF2α, and phosphorylated PKR (PKR∼P) and PKR.