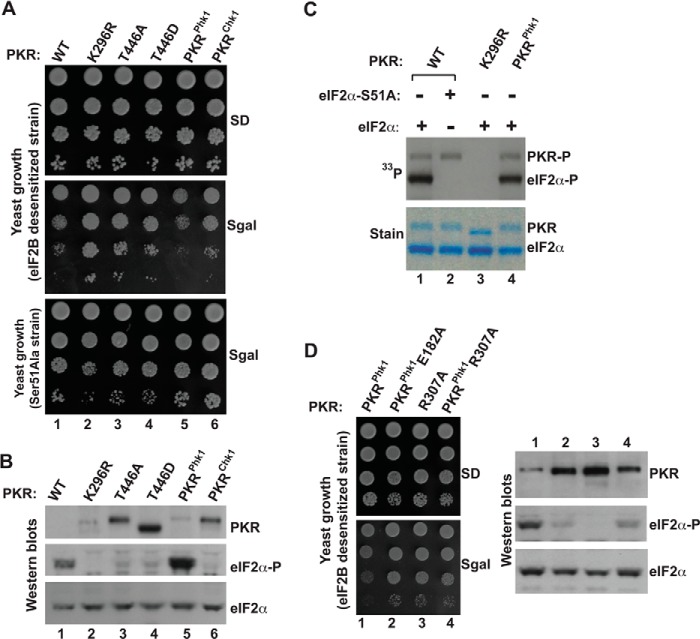
FIGURE 4.
Functional substitution of activation loop residues of PKR by residues from the activation loop of phosphorylase kinase 1 (Phk1). A, in vivo analysis of PKR mutants by growth in yeast. The yeast strain H17 (eIF2B desensitive) or MY71 (eIF2α-S51A) harboring indicated WT PKR and its derivatives were serially diluted and spotted on SD and SGal media. B, in vivo analysis of eIF2α phosphorylation by PKR mutants. Whole cell extracts were prepared from yeast cells indicated in A and subjected to Western blot analysis using phosphospecific antibodies against Ser-51 (eIF2α∼P). The membrane was stripped and re-probed with a polyclonal antibody of eIF2α and PKR. C, in vitro analysis of eIF2α phosphorylation by PKR mutants. Purified PKR protein (WT, K296R, or PKRphk1) was mixed with the recombinant eIF2α and [γ-33P]ATP in a reaction buffer for 10 min. The reaction products were then separated using SDS-PAGE. The gel was stained, dried, and subjected to autoradiography to monitor the incorporation of 33P in eIF2α proteins. D, catalytic function of PKRphk1 chimera requires an active interaction between the activation loop and the helix-αC. Left panels, eIF2B desensitive strain H17 expressing indicated PKR mutants were tested for growth on SD and SGal media. Right panels, yeast cells were grown in the presence of galactose (10%) and harvested after 2 h. Whole cell extracts were then prepared and subjected to Western blot analyses using antibodies of phosphorylated eIF2α (eIF2α∼P), eIF2α, and PKR.