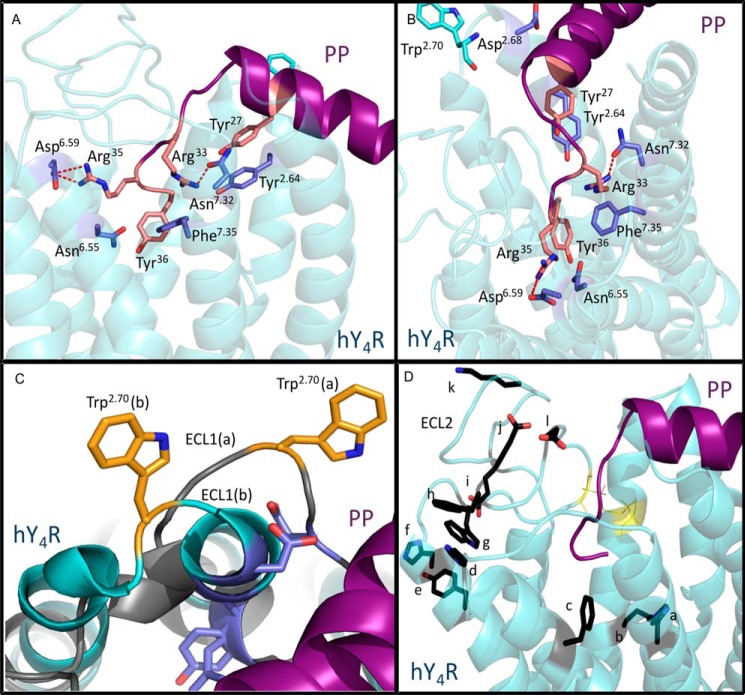
FIGURE 7.
Characterization of the binding pocket of PP docked in the hY4R comparative model. A, side view of PP (purple) docked to hY4R (cyan). Residues found to be important in the activation of hY4R by hPP are labeled. Predicted interactions are indicated by dotted red lines (salt bridge between Asp6.59 and Arg35 and hydrogen bond between Arg33 and Asn7.32). B, top-down view of the same docked model. C, two docked models show the variability in ECL1. The model shown in gray has a significantly longer ECL1 than that shown in cyan. Trp2.70, which was experimentally shown to be important in hY4R activation by PP, is shown to be in different proximity to PP depending on the size of ECL1. D, side view of the same docked model shown in A and B. Residues experimentally shown to be inactive in the binding of hPP to hY4R are indicated in black. The disulfide bond in ECL2 is also shown in yellow. a = His7.39; b = Gln3.32; c = Phe6.54; d = His6.62; e = Tyr5.38; f = His5.34; g = Trp5.29; h = Phe4.80; i = Glu4.67; j = Glu4.79; k = Lys4.72; and l = Asp4.83.