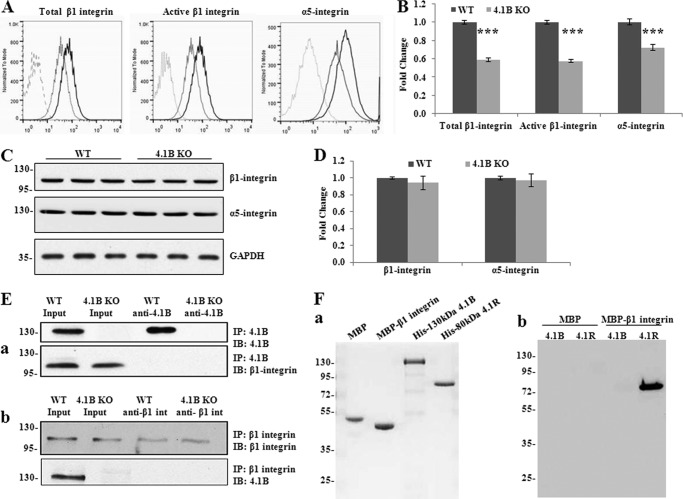
FIGURE 6.
Decreased surface expression and activity of β1 integrin accompanied with the loss of surface α5 integrin in 4.1B KO MEF cells. A and B, surface expression of β1 and α5 integrin. The representative profiles and quantitative analysis from three independent experiments are shown in A and B, respectively. Black line, WT; light gray, 4.1B KO; broken line, unstained. ***, p < 0.001. C and D, immunoblot analysis of β1 and α5 integrin. 40 μg of cell lysates were probed with anti-β1 integrin antibody and α5 integrin, respectively. GAPDH was used as the loading control (C). Quantitative analysis from three independent experiments was shown in D. E, immunoprecipitation (IP). a, 130-kDa 4.1B was immunoprecipitated from MEF cells using anti-4.1B HP antibody. 130-kDa 4.1B or β1 integrin in the immunoprecipitate was detected using anti-4.1B HP antibody or anti-β1 integrin antibody. IB, immunoblot. b, β1 integrin was immunoprecipitated from MEF cells using anti-β1 integrin antibody. β1 integrin or 130-kDa 4.1B in the immunoprecipitate was detected using the indicated antibodies. F, in vitro pulldown assay for β1 integrin-4.1B interaction. a, proteins used in the binding assays. 2 μg of each affinity-purified recombinant protein was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and stained with Gel Blue; from the left, as indicated: MBP, MBP-β1 integrin cytoplasmic domain fusion protein, His-tagged 130-kDa 4.1B, His-tagged 80 kDa 4.1R. b, analysis of binding. His-tagged constructs of 4.1B or 4.1R, as in a, were mixed with either MBP or MBP-β1 integrin cytoplasmic domain. The mixtures were incubated with amylose beads and centrifuged to recover bound complexes as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Bound complexes were removed from the beads by washing with SDS, and they were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-His tag antibody. Note that MPB-β1 integrin cytoplasmic domain binds to 4.1R but not 4.1B and that neither 4.1 protein binds MBP alone.