FIGURE 1.
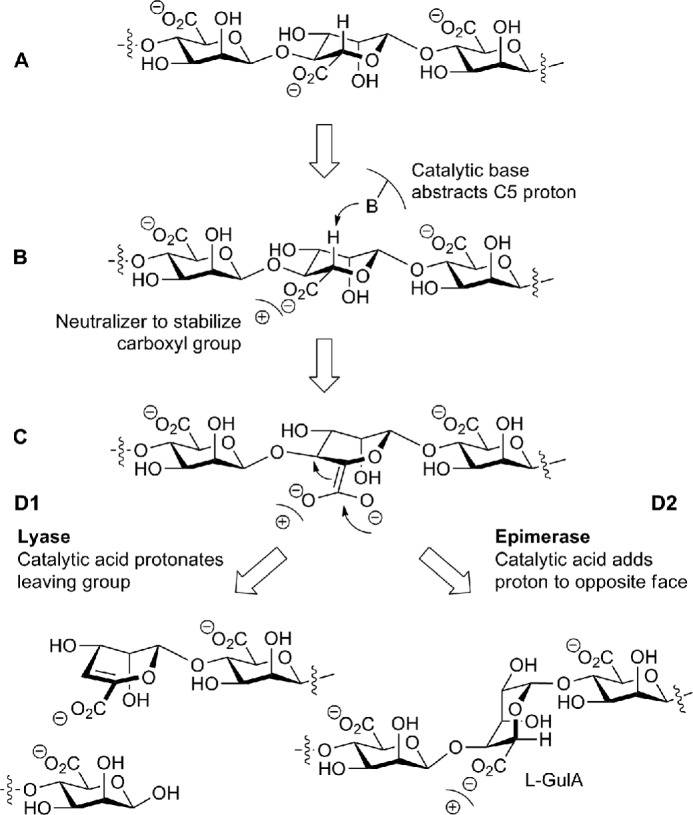
Lyase β-elimination and epimerase reaction mechanisms. A, a mannuronate residue within the mannuronate polymer is depicted. B, a positive charge stabilizes the carboxylate group while the catalytic base abstracts the C5 proton. C, an enolate group is formed. D1, a double bond between C4 and C5 is formed, the chain is cleaved, and the catalytic acid protonates the leaving group, forming a new reducing end. D2, a proton is added to the opposite face of the C5 by the catalytic acid, and the C5 epimer α-l-guluronate (l-GulA) is formed.
