Figure 4.
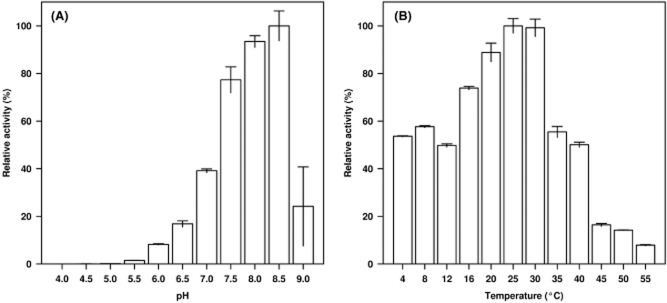
The wild-type CN1E1 α/β hydrolase pH (A) and temperature (B) profiles. Esterase activity using pNP-propionate (at 410 nm) was determined as described previously (Martínez-Martínez et al., 2013). The standard deviation (SD) for the triplicate assays is shown. We examined pH values between 4.0 and 9.5 and temperatures between 4 and 80°C to determine the optimal parameters. The following buffers were examined at 40 mM: sodium citrate (pH 4.0–4.5), sodium acetate (pH 5.0–6.0), 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES) (pH 5.5–6.0), piperazine-N,N′-bis(ethanesulfonic acid) (PIPES) (pH 6.0–7.0), 4-(2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) (pH 7.0–8.0), K/Na-phosphate (pH 7.5), Tris-HCl (pH 8.5) and glycine (pH 9.0–9.5). The pH was adjusted at 25°C. The pH and temperature profiles were collected at 40°C (panel A) and pH 7.0 (using 40 mM HEPES; panel B) respectively. In panels (A) and (B), 100% of the activity refers to 27.08 ± 1.80 and 21.17 ± 1.41 units mg−1 respectively.
