Figure 5.
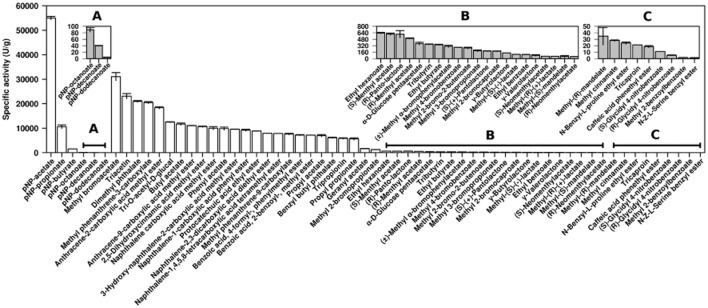
Substrate profile for the wild-type CN1E1 α/β hydrolase using a set of structurally diverse esters. The specific activities were calculated in triplicate as described by Martínez-Martínez and colleagues (2013) at 40°C in 20 mM HEPES buffer pH 7.0 (for pNP esters) or 5 mM EPPS buffer pH 8.0 (for the remaining esters). The standard deviation (SD) for the triplicate assays is shown. The chemicals used for the enzymatic experiments were the purest grade available and were purchased from Fluka-Aldrich-Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). The hydroxycinnamic-like esters were supplied by Apin Chemicals (Oxon, UK), the methyl phenanthrene-3-carboxylate and methyl phenanthrene-9-carboxylate were supplied by Wuhan Farthest Chemical (Mainland, China), and the anthracene-9-carboxylic acid methyl ester and anthracene-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester were obtained from Alfa Aesar (Karlsruhe, Germany). Insets (A) to (C) in the figure represent a zoom for substrates hydrolysed at low rates.
