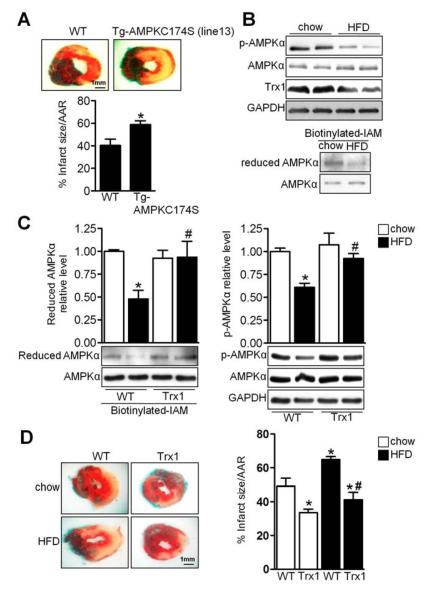
Figure 7. HFD Induced AMPK Oxidation in Vivo.
(A) Tg-AMPKC174S and WT mice were subjected to ischemia for 3 h. Myocardial infarct area/area at risk (% infarct size/AAR) is shown (*p<0.05 vs. WT, n=7). (B–C) Tg-Trx1 and WT mice on C57BL/6J background were fed chow or HFD for 20 weeks. Heart lysates were analyzed by immunoblot for p-AMPKα, AMPKα, Trx1, and GAPDH. The extent of AMPKα cysteine reduction was analyzed. Statistical analyses of densitomeric measurements of reduced AMPKα and p-AMPKα are shown (*p<0.05 vs. WT/chow, #p<0.05 vs. WT/HFD, n=3–4). (D) Tg-Trx1 and WT mice were fed chow or HFD for 20 weeks and subjected to ischemia for 3 h. Myocardial infarct area/area at risk (% infarct size/ARR) is shown (*p<0.05 vs. WT/chow, #p<0.05 vs. WT/HFD, n=5). Error bars represent SEM.