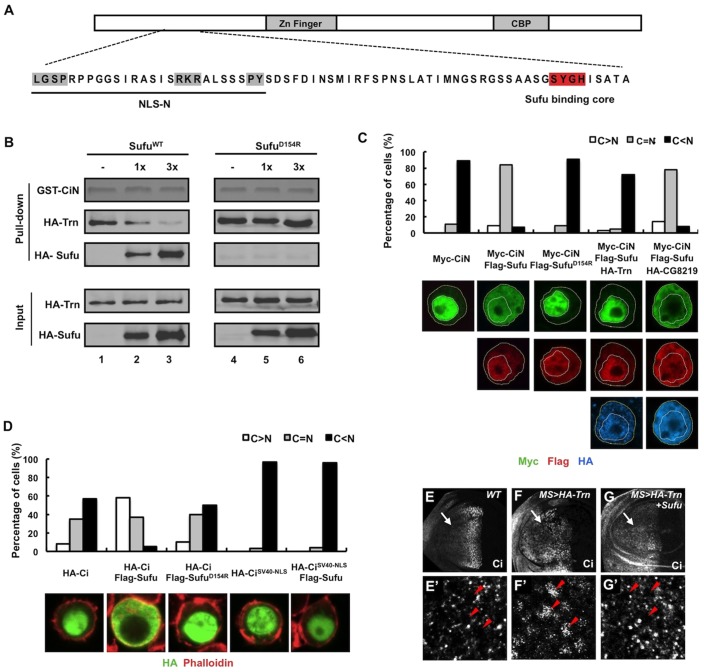
Fig. 5.
Sufu inhibits Ci nuclear translocation by blocking the interaction of Trn and Ci. (A) Structure of Ci with sequence of the NR region indicated underneath. The PY-NLS motif is highlighted in gray and the Sufu-binding core in red. (B) Binding of Sufu to CiN precludes Trn binding. Equal amounts of GST–CiN bound to Glutathione beads were incubated with a fixed amount of purified HA–Trn without or with increasing amounts of purified HA–SufuWT or HA–SufuD154R. Pull-down and input proteins were analyzed by western blot. GST–CiN was visualized by Coomassie Blue staining. (C) Quantification of subcellular localization of CiN. 100 cells were randomly picked for each transfection and categorized based on the differential nuclear/cytoplasmic distributions of Myc signal. Representative images of S2 cells transfected with the indicated constructs and immunostained with anti-Myc (green), anti-FLAG (red) and anti-HA (blue) antibodies are shown below. Yellow and white dashed lines outline cellular and nuclear membrane, respectively. (D) Quantification of subcellular localization of Ci and CiSV40-NLS. 100 cells were randomly picked for each transfection and categorized based on the differential nuclear and cytoplasmic distributions of HA signal. Representative images of S2 cells transfected with HA–Ci or HA–CiSV40-NLS either alone or with FLAG–Sufu or FLAG–SufuD154R. The transfected cells were treated with 10 ng/ml LMB for 2 hours before immunostaining with an anti-HA antibody (green) and Phalloidin (red). (E–G′) Low (E–G) and high (E′–G′) magnification views of a wild-type wing disc (E,E′), a wing disc expressing HA–Trn (F,F′), and a wing disc coexpressing HA–Trn and Sufu (G,G′) with MS1096 treated with 50 ng/ml LMB for 2 hours prior to immunostaining with an anti-Ci (red) antibody. Arrows indicate the anterior compartments; arrowheads indicate nuclei. Coexpression of Sufu blocked Trn-induced nuclear localization of Ci in A-compartment cells away from the A/P boundary.