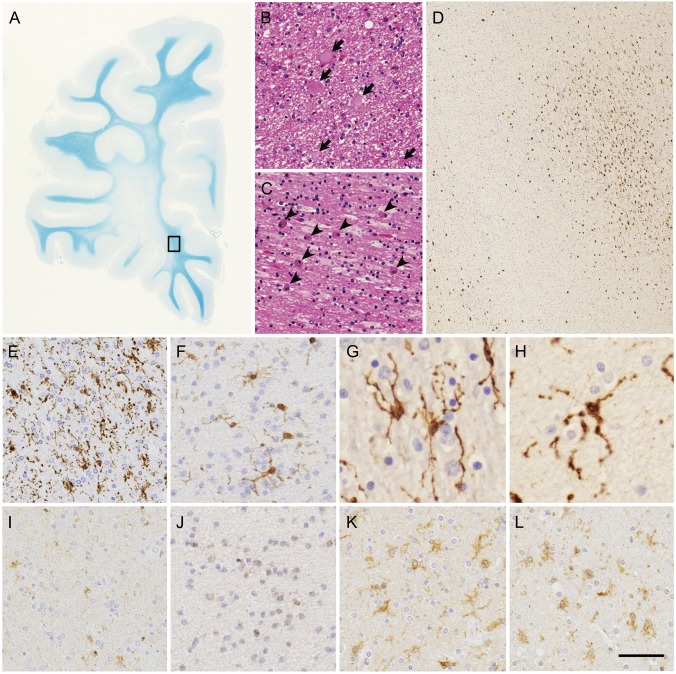
Figure 4. Histopathologic features of patients with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids.
(A–C) White matter lesions of frontal lobe of patient VI. (A) Marked myelin loss of white matter with U-fibers spared. (B) Axonal spheroids (arrows) in white matter. (C) Abundant macrophages (arrowheads) in white matter. (D–L) Microglia in white matter of patients with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids and control brains. (D-H) Immunohistochemistry of Iba1 in degenerative white matter. (D, E) Patient VI. (F) Patient III. (G) Patient IHC1. (H) Patient IHC2. (D) The boxed area in (A) is enlarged. Spatially restricted appearance of Iba1-immunopositive activated microglia (upper right corner). (E–H) Characteristic features of microglia. (I–L) CSF-1R immunohistochemistry in degenerative white matter. (I) Patient VI. (J) Patient III. (K) Patient with Alzheimer disease. (L) Patient with adrenoleukodystrophy. Images in I and J were taken from serial sections of images in E and F, respectively. Note very faint or no CSF-1R immunopositivity in activated microglia in images I and J. (A) Klüver-Barrera staining, (B, C), hematoxylin & eosin staining, (D–L) immunohistochemistry of Iba1 (D–H) and CSF-1R (I–L). Bar = 7 mm for A, 33 μm for B and C, 306 μm for D, 50 μm for E, F, and I–L, and 25 μm for G and H.