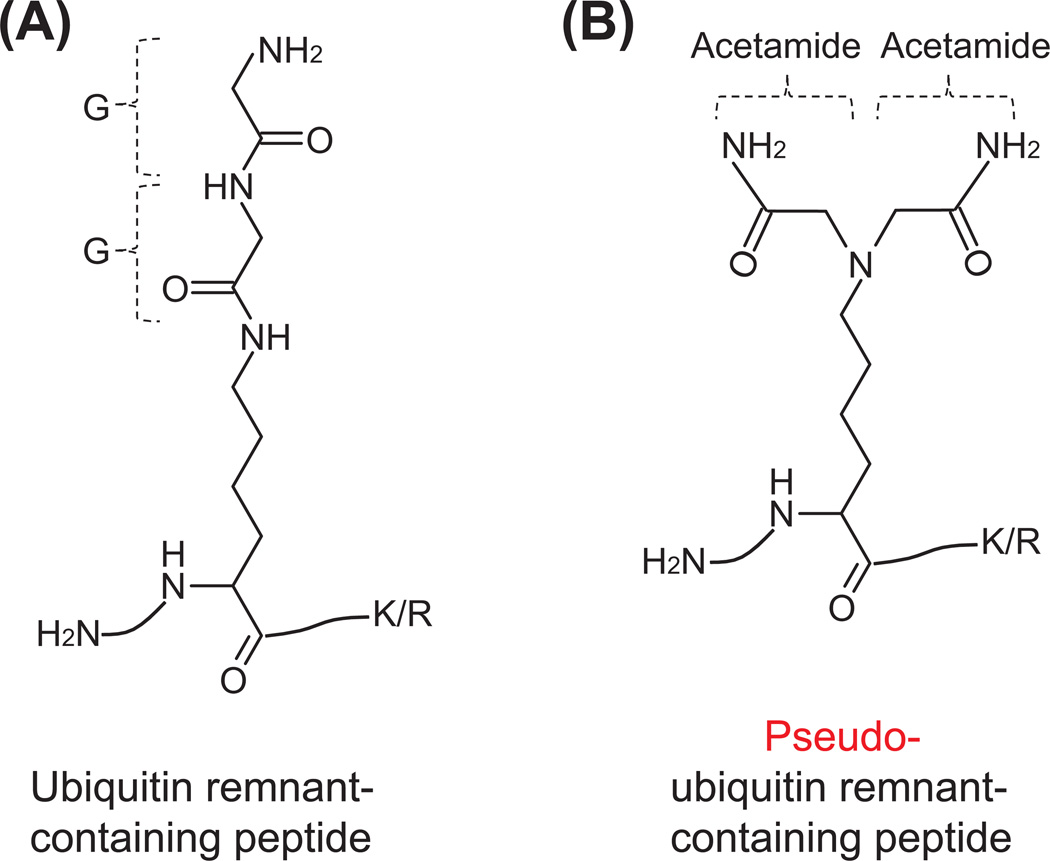
Figure 8. Chemical structure of ubiquitin remnant-containing peptides (A) and pseudo-ubiquitin remnant-containing peptides (B).
The ubiquitin remnant-containing peptides are mainly derived from trypsin digestion of ubiquitinated proteins. The pseudo-ubiquitin remnant-containing peptides are potentially introduced during the alkylation of thiols with iodoacetamide at high concentrations and high temperatures. Both adducts have same chemical formula but different chemical structures. The anti-diglycyl lysine antibody can recognize and immunoprecipitate peptide A but not peptide B. In addition, the formation of pseudo-ubiquitin remnant-containing peptides during sample preparation can be eliminated when the alkylation step is carried out at low concentrations of iodoacetamide and at low temperatures. Alternatively, the replacement of iodoacetamide with a more specific alkylating agent, chloroacetamide, can prevent the generation of pseudo-ubiquitin remnant-containing peptides.