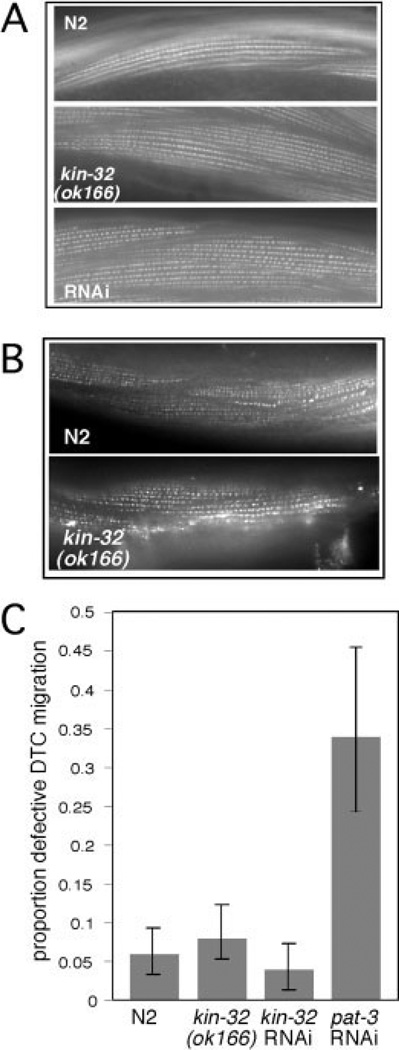
Fig. 4.
kin-32(ok166) and kin-32 RNA interference (RNAi) -treated muscles and gonads are not significantly different from N2. A: Rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin was used to stain actin filaments in body wall muscle cells of N2 animals (top), kin-32(ok166) animals (middle), and kin-32 RNAi-treated animals (bottom). B: Anti-α-actinin (MH35) antibodies were used to stain dense body structures in the muscle cells of N2 animals (top) or kin-32(ok166) animals (bottom). C: kin-32(ok166), kin-32 RNAi-treated, and N2 hermaphrodites were examined for defects in gonad formation. Feeding RNAi for pat-3/β-integrin was used as a positive control. Number of gonad arms assayed (N): N2, N = 314; kin-32(ok166) N = 216; kin-32 RNAi N = 196; pat-3 RNAi N=82. Percentage of animals with misshapen gonad arms is indicated by the shaded bars, and the error bars indicate the 95% confidence interval.