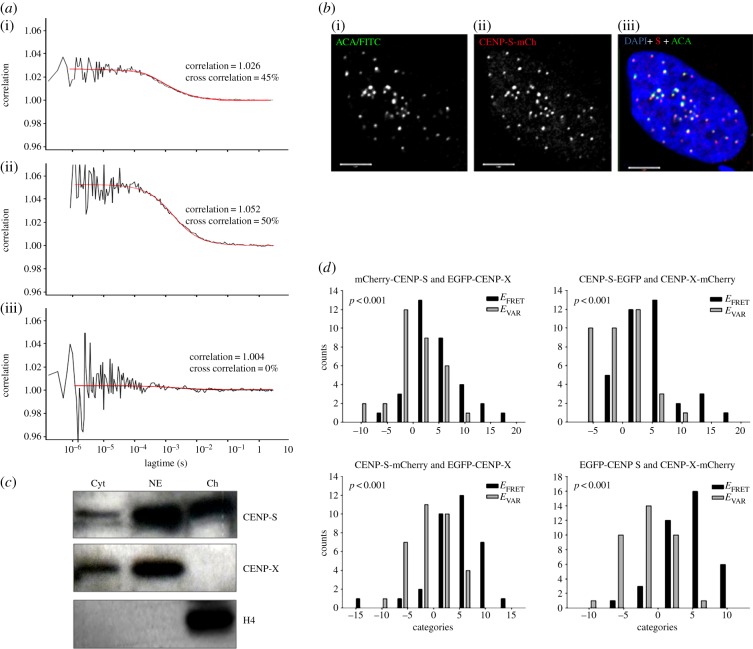
Figure 1.
CENP-S and CENP-X exist primarily in a heterotypic complex in solution and at centromeres. (a) FCCS analysis of EGFP-mRFP fusion protein (i), EGFP-CENP-X and mCherry-CENP-S (ii) and EGFP + mRFP (iii) in the cell nucleus. The cross-correlation function (black line) results from the correlation of the autocorrelation functions of EGFP and mCherry/mRFP as described in the text, while the red line shows the fitted curve derived from the cross-correlation values. The number of co-localized molecules for EGFP-CENP-X + mCherry-CENP-S (50%) and the positive control (45%) is similar, indicating CENP-S/-X co-localization. (b) Immunofluorescence confirms that CENP-FP constructs target normally to centromeres. U2OS cells transfected with CENP-S-mCherry were immunostained with anticentromere antibodies (i), revealing co-localization with CENP-S-mCherry (ii) within the nucleus (DAPI; (iii)). Comparable results were observed with CENP-X-FP constructs. (c) Partitioning of CENP-S and CENP-X in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic proteins (Cyt) were separated from nuclei, which were further extracted with 0.35 M NaCl to generate a nuclear extract (NE) and chromatin-bound (Ch) fractions and probed by western blot to detect CENP-S, CENP-X and histone H4. (d) FRET analysis reveals the association of the CENP-S/CENP-X complex at centromeres.