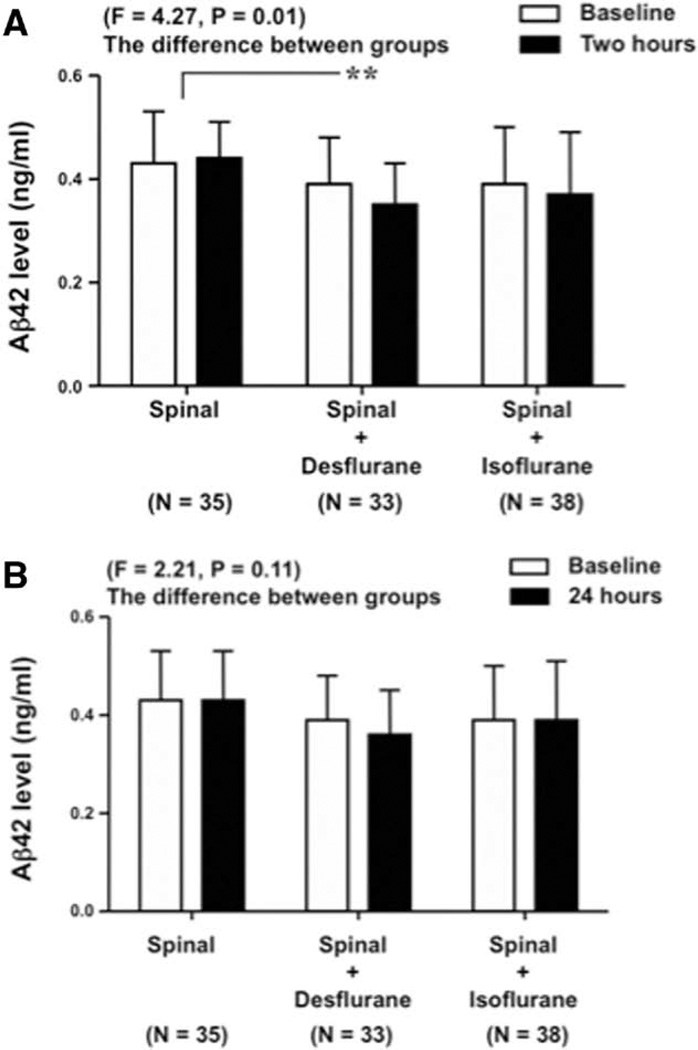
Fig. 2.
Surgery under desflurane anesthesia is associated with decreases in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) β-amyloid protein (Aβ)42 levels 2 h after the anesthesia. The preop-erative baseline, the 2- and 24-h postoperative human CSF Aβ42 levels following spinal (S), spinal plus desflurane (SD), and spinal plus isoflurane (SI) anesthesia are presented. A, The differences between the 2-h postoperative and the preoperative baseline human CSF Aβ42 levels are significantly different among the S, SD, or SI anesthesia group (F = 4.27, P = 0.01). Specifically, the difference between the 2-h postoperative and the preoperative baseline human CSF Aβ42 levels following SD anesthesia is negatively greater than that following S anesthesia (F = 8.41, ** P = 0.004). B, The differences between the 24-h postoperative and the preoperative baseline human CSF Aβ42 levels are not significantly different among the S, SD, or SI anesthesia group (F = 2.21, P = 0.11).